(Shrink image) |
mNo edit summary |
||
| (2 intermediate revisions by 2 users not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
{{header|docs}} | {{header|docs}} | ||
{{Draft}} | |||
<span style="color: red; font-weight: bold;"> Comments Welcome </span> | |||
== Normal translation path == | == Normal translation path == | ||
| Line 16: | Line 18: | ||
== How to set up your document with Transifex == | |||
For help on how to use Transifex with your document, see [[Setting up a document with Transifex]]. | |||
[[Category:Docs Project process]] | [[Category:Docs Project process]] | ||
Latest revision as of 14:34, 16 August 2011
Comments Welcome
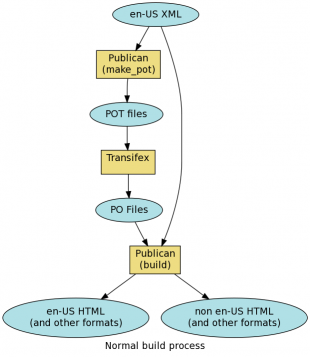
Normal translation path
Publican not only converts the XML to various output formats. It is also capable of producing a file called the POT file which contains a list of all strings in the document. Translators take this document and produce a PO file, which contains the english language for each string, followed by the same string in the target language. Publican can then take this file, along with the English XML file, and produce the target formats in the desired language.
Typically, the translators use an online application called Transifex to help track the translation process and to interface with the documentation repositories.
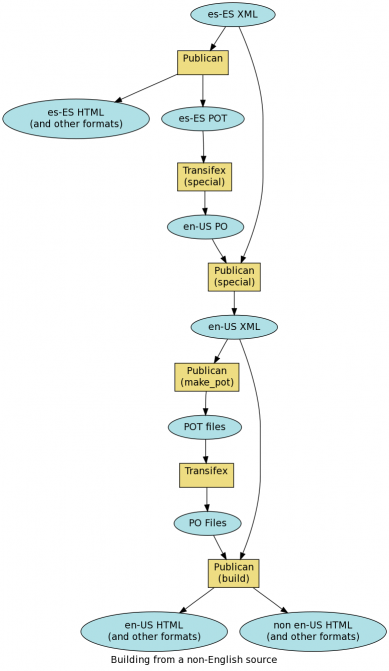
Non-English source
Sometimes it is desirable to originally produce the document in a language other than English. In this case, the initial translation is made to English, and then from English to the other target languages. This is necessary since translators typically work from English. English to, say, Greek translators can be found, but getting a Greek to Tamil translator might be something of a challenge.
How to set up your document with Transifex
For help on how to use Transifex with your document, see Setting up a document with Transifex.

