(Created page with "= '''Firefox Hardware acceleration on Fedora''' = Firefox supports hardware acceleration on Linux so let's look how to configure it and diagnose potential issues. == Web pag...") |
No edit summary |
||
| (50 intermediate revisions by 14 users not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
= '''Firefox Hardware acceleration on Fedora''' = | = '''Firefox Hardware acceleration on Fedora''' = | ||
Firefox supports hardware acceleration on Linux so let's look how to configure it and diagnose potential issues. | Firefox on Fedora supports hardware acceleration on Linux so let's look how to configure it and diagnose potential issues. This guide is adjusted for Fedora only and may not work for stock Mozilla binaries or other distros. | ||
== Web page rendering == | == Web page rendering == | ||
Accelerated web page rendering is supported on both X11 and Wayland backends via | Accelerated web page rendering is supported on both X11 and Wayland backends via [https://mastransky.wordpress.com/2021/01/10/firefox-were-finally-getting-hw-acceleration-on-linux/ '''WebRender''']. | ||
Please note that Firefox requires a GPU with support for OpenGL 3.2 or newer or GLES 3.0 or newer to enable hardware acceleration ([https://bugzilla.mozilla.org/show_bug.cgi?id=1748819#c4 Source and further info]). You can check your hardware using `glxinfo | grep "profile version"` for OpenGL and `eglinfo | grep version` for GLES. | |||
You can check hardware acceleration state at '''about:support''' page, look at '''Compositing''' row. If there's '''WebRender''', you're running on hardware. If there's '''WebRender (software)''' you're on non-accelerated backend. | You can check hardware acceleration state at '''about:support''' page, look at '''Compositing''' row. If there's '''WebRender''', you're running on hardware. If there's '''WebRender (software)''' you're on non-accelerated backend. | ||
[[File:Webrender-about.png|thumb|center|WebRender Firefox setup]] | |||
=== Web page rendering on Wayland === | === Web page rendering on Wayland === | ||
Hardware acceleration should work out-of-the-box on Wayland. If not please [https://bugzilla.mozilla.org file a bug] for it. | Hardware acceleration should work out-of-the-box on Wayland. If not please [https://bugzilla.mozilla.org/enter_bug.cgi?product=Core&component=Graphics%3A+WebRender file a bug] for it. | ||
=== Web page rendering on X11 === | === Web page rendering on X11 === | ||
X11 backend can tun in two modes - [https://mastransky.wordpress.com/2021/10/30/firefox-94-comes-with-egl-on-x11/ '''EGL and XGL''']. | X11 backend can tun in two modes - [https://mastransky.wordpress.com/2021/10/30/firefox-94-comes-with-egl-on-x11/ '''EGL and XGL''']. You should be on '''EGL''' unless you're running on unsupported config (old NVIDIA drivers, NVIDIA drivers on XWayland or so). | ||
=== Force disable hardware acceleration === | |||
For testing purposes you can disable hardware WebRender. Go to '''about:config''' page, set '''gfx.webrender.software''' to '''true''' and restart browser. There should be '''WebRender (software)''' at '''about:support''' page then. | |||
== Video decoding == | == Video decoding == | ||
Hardware accelerated video decoding (for video playback or for WebRTC) is [https://mastransky.wordpress.com/2020/09/29/firefox-81-on-fedora-with-va-api-webrtc-and-x11/ available ] via VA-API for both X11 and Wayland. Since '''firefox-101.0.1-4''' package it's enabled by default for Intel/AMD users. | |||
You can check VA-API acceleration state at '''about:support''' page, look at '''HARDWARE_VIDEO_DECODING''' row. If there's '''available by default''', you're running on hardware by default. | |||
[[File:Firefox-VAAPI-Screenshot1.png|thumb|center|Correct VA-API setup]] | |||
You can '''disable''' it at '''about:config''' page setting '''media.hardware-video-decoding.enabled''' to '''false'''. | |||
You may install [https://addons.mozilla.org/en-US/firefox/addon/enhanced-h264ify/ enhanced-h264ify] Firefox extension to disable non-accelerated video formats. | |||
=== Configure VA-API Video decoding on AMD === | |||
Accelerated video decoding works well on AMD as free drivers are available. Free video formats (e.g. VP8/VP9/AV1) should be accelerated out of the box. You can add support for H.264 VA-API decode by these steps: | |||
* Install '''ffmpeg-free''' from Fedora, install '''libavcodec-freeworld''' and '''mesa-va-drivers-freeworld'''. See [https://rpmfusion.org/Howto/Multimedia#Hardware_codecs_with_AMD_.28mesa.29 RPM Fusion howto] (section ''Hardware codecs with AMD (mesa)'') for instructions. It's needed for VA-API H.264 decoding. | |||
* Run '''vainfo''' on terminal to verify that [https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Video_Acceleration_API VA-API works]. | |||
* Restart browser. | |||
=== Configure VA-API Video decoding on Intel === | |||
Accelerated video decoding works well on most Intel GPUs as free drivers are available. There are two<ref>There's also ''libva-intel-hybrid-driver'', but that only adds support for VP8 encoding and VP9 decoding with selected chips.</ref> drivers for Intel cards, '''libva-intel-driver''' (provides i965_drv_video.so) and '''[https://github.com/intel/media-driver intel-media-driver]''' (iHD_drv_video.so, a.k.a. "iHD", for recent<ref>''intel-media-driver'' is recommended for Intel "Broadwell (5th gen) and newer" chipsets, particularly Ice Lake (10th gen) and newer.</ref> chipsets). Currently, Firefox works with either '''libva-intel-driver''' or '''intel-media-driver'''. | |||
To determine which codecs your hardware supports, refer to: | |||
* The [https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Intel_Quick_Sync_Video#Hardware_decoding_and_encoding Intel chipsets video features table] on Wikipedia | |||
* The [https://github.com/intel/media-driver#components-and-features features table] in the intel-media-driver's readme on GitHub | |||
You can enable VA-API on Intel with these steps: | |||
* Install '''ffmpeg-free''' from Fedora, install '''libavcodec-freeworld''' from [https://rpmfusion.org/ RPM Fusion repository] for H.264 decoding. | |||
* Install '''libva-intel-driver''' or '''intel-media-driver''' package (depending on your chipset) to enable VA-API on Intel. | |||
* In a terminal, run '''vainfo''' to verify that [https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Video_Acceleration_API VA-API] works. If VA-API is disabled you're probably running on new hardware and you need '''intel-media-driver''' from [https://rpmfusion.org/ RPM Fusion repository non-free]. When running the newer driver, you may need to specify the "iHD" driver when running the vainfo command, like so: '''LIBVA_DRIVER_NAME=iHD vainfo''' | |||
* Restart browser. | |||
=== Configure VA-API Video decoding on NVIDIA === | |||
Accelerated video decoding works on NVIDIA proprietary drivers thanks to '''Stephen "elFarto"''' and his [https://github.com/elFarto/nvidia-vaapi-driver '''nvidia-vaapi-driver project''']. It's VA-API implemention using NVIDIA's NVDEC decoder. | |||
You can enable VA-API on NVIDIA / Fedora 37 by these steps: | |||
* Install [https://rpmfusion.org/Howto/NVIDIA NVIDIA proprietary drivers]. Don't forget to install cuda/nvdec/nvenc support. | |||
* Install '''ffmpeg-free''' from Fedora, install '''libavcodec-freeworld''' from [https://rpmfusion.org/ RPM Fusion repository] for H.264 decoding. | |||
* Install '''nvidia-vaapi-driver''' from [https://rpmfusion.org/ RPM Fusion repository non-free]. Don't use Fedora provided '''libva-vdpau-driver''' package as it's old and broken. | |||
* Run Firefox and force enable VA-API as it's disabled on NVIDIA by default. Go to '''about:config''' page and set '''media.ffmpeg.vaapi.enabled''' to '''true'''. | |||
* Run Firefox with '''NVD_BACKEND=direct MOZ_DISABLE_RDD_SANDBOX=1''' env variables. | |||
== Troubleshooting == | |||
* Verify you're running on HW accelerated backend ('''WebRender''') under '''Wayland''' or '''X11/EGL''' at '''about:support'''. | |||
* Run '''vainfo''' on terminal to verify that [https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Video_Acceleration_API VA-API works]. | |||
* Run Firefox on terminal with '''MOZ_LOG="FFmpegVideo:5"''' env variable. It produces a playback and decode log with VA-API / ffmpeg details. | |||
* VA-API is also used for WebRTC (video conferencing like Google Meet, Zoom, Bluejeans). If you see any video artifacts you can disable VA-API for it. At '''about:config''' page set '''media.navigator.mediadatadecoder_vpx_enabled''' to '''false''' and restart browser. | |||
* Test different VA-API capable player, for instance mpv by running '''mpv --hwdec=vaapi test_clip''' on terminal. | |||
* You may also want to reset custom changes that may be intervening with HW acceleration. To do that, go to '''about:support''' and click Refresh Firefox. | |||
== Video encoding == | == Video encoding == | ||
Hardware accelerated video encoding (for WebRTC for instance) is not supported/implemented in Firefox, no matter which preference you set at '''about:config''' page. | |||
Latest revision as of 07:17, 7 May 2024
Firefox Hardware acceleration on Fedora
Firefox on Fedora supports hardware acceleration on Linux so let's look how to configure it and diagnose potential issues. This guide is adjusted for Fedora only and may not work for stock Mozilla binaries or other distros.
Web page rendering
Accelerated web page rendering is supported on both X11 and Wayland backends via WebRender.
Please note that Firefox requires a GPU with support for OpenGL 3.2 or newer or GLES 3.0 or newer to enable hardware acceleration (Source and further info). You can check your hardware using glxinfo | grep "profile version" for OpenGL and eglinfo | grep version for GLES.
You can check hardware acceleration state at about:support page, look at Compositing row. If there's WebRender, you're running on hardware. If there's WebRender (software) you're on non-accelerated backend.
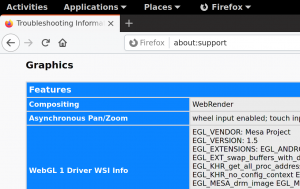
Web page rendering on Wayland
Hardware acceleration should work out-of-the-box on Wayland. If not please file a bug for it.
Web page rendering on X11
X11 backend can tun in two modes - EGL and XGL. You should be on EGL unless you're running on unsupported config (old NVIDIA drivers, NVIDIA drivers on XWayland or so).
Force disable hardware acceleration
For testing purposes you can disable hardware WebRender. Go to about:config page, set gfx.webrender.software to true and restart browser. There should be WebRender (software) at about:support page then.
Video decoding
Hardware accelerated video decoding (for video playback or for WebRTC) is available via VA-API for both X11 and Wayland. Since firefox-101.0.1-4 package it's enabled by default for Intel/AMD users.
You can check VA-API acceleration state at about:support page, look at HARDWARE_VIDEO_DECODING row. If there's available by default, you're running on hardware by default.
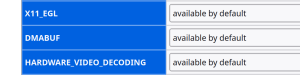
You can disable it at about:config page setting media.hardware-video-decoding.enabled to false.
You may install enhanced-h264ify Firefox extension to disable non-accelerated video formats.
Configure VA-API Video decoding on AMD
Accelerated video decoding works well on AMD as free drivers are available. Free video formats (e.g. VP8/VP9/AV1) should be accelerated out of the box. You can add support for H.264 VA-API decode by these steps:
- Install ffmpeg-free from Fedora, install libavcodec-freeworld and mesa-va-drivers-freeworld. See RPM Fusion howto (section Hardware codecs with AMD (mesa)) for instructions. It's needed for VA-API H.264 decoding.
- Run vainfo on terminal to verify that VA-API works.
- Restart browser.
Configure VA-API Video decoding on Intel
Accelerated video decoding works well on most Intel GPUs as free drivers are available. There are two[1] drivers for Intel cards, libva-intel-driver (provides i965_drv_video.so) and intel-media-driver (iHD_drv_video.so, a.k.a. "iHD", for recent[2] chipsets). Currently, Firefox works with either libva-intel-driver or intel-media-driver.
To determine which codecs your hardware supports, refer to:
- The Intel chipsets video features table on Wikipedia
- The features table in the intel-media-driver's readme on GitHub
You can enable VA-API on Intel with these steps:
- Install ffmpeg-free from Fedora, install libavcodec-freeworld from RPM Fusion repository for H.264 decoding.
- Install libva-intel-driver or intel-media-driver package (depending on your chipset) to enable VA-API on Intel.
- In a terminal, run vainfo to verify that VA-API works. If VA-API is disabled you're probably running on new hardware and you need intel-media-driver from RPM Fusion repository non-free. When running the newer driver, you may need to specify the "iHD" driver when running the vainfo command, like so: LIBVA_DRIVER_NAME=iHD vainfo
- Restart browser.
Configure VA-API Video decoding on NVIDIA
Accelerated video decoding works on NVIDIA proprietary drivers thanks to Stephen "elFarto" and his nvidia-vaapi-driver project. It's VA-API implemention using NVIDIA's NVDEC decoder.
You can enable VA-API on NVIDIA / Fedora 37 by these steps:
- Install NVIDIA proprietary drivers. Don't forget to install cuda/nvdec/nvenc support.
- Install ffmpeg-free from Fedora, install libavcodec-freeworld from RPM Fusion repository for H.264 decoding.
- Install nvidia-vaapi-driver from RPM Fusion repository non-free. Don't use Fedora provided libva-vdpau-driver package as it's old and broken.
- Run Firefox and force enable VA-API as it's disabled on NVIDIA by default. Go to about:config page and set media.ffmpeg.vaapi.enabled to true.
- Run Firefox with NVD_BACKEND=direct MOZ_DISABLE_RDD_SANDBOX=1 env variables.
Troubleshooting
- Verify you're running on HW accelerated backend (WebRender) under Wayland or X11/EGL at about:support.
- Run vainfo on terminal to verify that VA-API works.
- Run Firefox on terminal with MOZ_LOG="FFmpegVideo:5" env variable. It produces a playback and decode log with VA-API / ffmpeg details.
- VA-API is also used for WebRTC (video conferencing like Google Meet, Zoom, Bluejeans). If you see any video artifacts you can disable VA-API for it. At about:config page set media.navigator.mediadatadecoder_vpx_enabled to false and restart browser.
- Test different VA-API capable player, for instance mpv by running mpv --hwdec=vaapi test_clip on terminal.
- You may also want to reset custom changes that may be intervening with HW acceleration. To do that, go to about:support and click Refresh Firefox.
Video encoding
Hardware accelerated video encoding (for WebRTC for instance) is not supported/implemented in Firefox, no matter which preference you set at about:config page.

