Liangsuilong (talk | contribs) No edit summary |
Liangsuilong (talk | contribs) No edit summary |
||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
koji 简介 | |||
== koji 简介 == | |||
Koji 是 Fedora 的包编译管理工具,主页在: https://fedorahosted.org/koji/wiki | Koji 是 Fedora 的包编译管理工具,主页在: https://fedorahosted.org/koji/wiki | ||
在线资源 | '''在线资源''' | ||
Build Packages for Fedora Using Koji | Build Packages for Fedora Using Koji | ||
Run Your Own Koji Build Server | Run Your Own Koji Build Server | ||
术语 [ Terminology ] | |||
== Koji 架构 == | |||
'''术语''' [ Terminology ] | |||
Koji 中有时需要分清通常的 package ,一个包的特定 build ,和一个 build 产生的各种 rpm 文件。下面详细解释: | Koji 中有时需要分清通常的 package ,一个包的特定 build ,和一个 build 产生的各种 rpm 文件。下面详细解释: | ||
Revision as of 16:13, 13 November 2009
koji 简介
Koji 是 Fedora 的包编译管理工具,主页在: https://fedorahosted.org/koji/wiki
在线资源
Build Packages for Fedora Using Koji Run Your Own Koji Build Server
Koji 架构
术语 [ Terminology ]
Koji 中有时需要分清通常的 package ,一个包的特定 build ,和一个 build 产生的各种 rpm 文件。下面详细解释:
Package rpm 的名字(仅仅name字段!)。严格区分的情况下,仅指代不带 任何其他信息的通常包名。如: kernel , glibc 等等 Build 包的一个特定 build。这里指代:所有架构和子包(即version和 release),子包指一个包编译后生成的很多其他包,也即同一个srpm生成的 所有包。例如:kernel-2.6.9-34.EL , glibc-2.3.4-2.19 RPM 一个特定的 rpm。 例如: kernel-2.6.9-34.EL.x86_64,kernel-devel-2.6.9-34.EL.s390, glibc-2.3.4-2.19.i686,glibc-common-2.3.4-2.19.ia64 Koji 组成 [ Components ]
Koji 包含几个部分 :
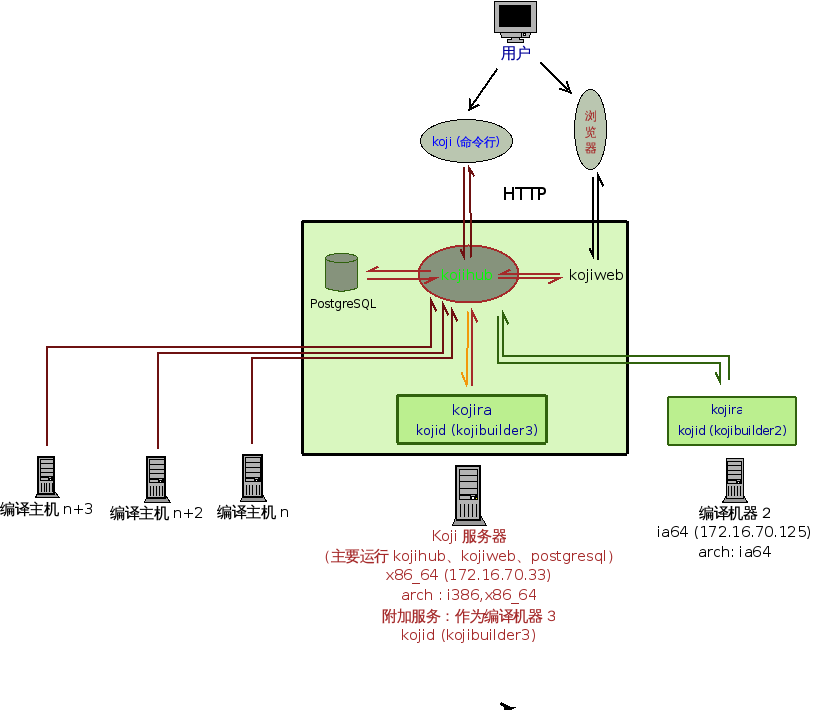
koji-hub 它是所有 Koji 操作的核心,通过 XML-RPC 运行于 Apache 的 mod_python 模块下。koji-hub 采用被动方式,仅仅接受 XML-RPC 请求,依 赖编译守护模块和其他模块来进行交互。koji-hub是唯一直接访问数据库的 模块,而且是有读写文件系统的权限的两个模块之一(另外一个是koji)。 kojid 它是编译守护模块,运行在每一个执行编译任务的机器上。主要任务 是对编译请求分析处理。Koji除了编译外也支持其他任务,如创建安装 images。kojid同样也可以完成这样的任务。kojid使用mock来编译。它为每 一个build创建一个干净的编译环境。kojid使用python编写,通过 XML-RPC 和 koji-hub 通信。 koji-web 它包含一套脚本,运行在 mod_python 下,使用 Cheetah 模板引 擎为 Koji 提供一个 Web 接口。 koji 它是一个用 python 写的 CLI 程序,提供对于 Koji 最多的操作。它 能让用户查询信息,也能执行编译操作。 kojira 它是一个后台守护程序,可以实时更新 build root repodata 一个示例架构图
包管理和组织 [ Package Organization ]
Tags 和 Targets
Koji 使用 tags 管理包。在 Koji 里,一个 tag 非常类似一个蜂箱,但是有下 面一些区别:
Tags 存在数据库中,而不是存在磁盘上。 Tags 支持多继承 每个 Tags 有自己的有效 packages 列表。(可继承) Package 所有权可以在没有 Tag 里设置。(可继承) Tag 继承是可以配置的。 你编译的时候针对的是 target 而不是 tag。 一个 build target 匹配一个包在哪里被编译,还包括这个包后来怎样被打上 tag。 通过下面命令可以得到 build target 的完全列表:
[root@localhost ~]# koji list-targets Name Buildroot Destination
dist-4E-epel dist-4E-epel-build dist-4E-epel dist-5E-epel dist-5E-epel-build dist-5E-epel dist-f10 dist-f10-build dist-f10 dist-f10-updates-candidate dist-f10-build dist-f10-updates-candidate dist-f11 dist-f11-build dist-f11 dist-f11-rebuild dist-f11-build dist-f11-rebuild dist-f11-updates-candidate dist-f11-build dist-f11-updates-candidate dist-f12 dist-f12-build dist-f12 dist-f8 dist-f8-build dist-f8 dist-f9 dist-f9-build dist-f9 dist-f9-updates-candidate dist-f9-build dist-f9-updates-candidate dist-f9-upstart dist-f9-build dist-f9-upstart dist-fc6 dist-fc6-build dist-fc6 dist-olpc2 dist-olpc2-build dist-olpc2 dist-olpc3 dist-olpc3-build dist-olpc3-devel dist-olpc4 dist-olpc4-build dist-olpc4 dist-rawhide dist-rawhide dist-rawhide f7-final f7-final f7-final f9-alpha f9-alpha f9-alpha olpc2-ship2 olpc2-ship2 olpc2-ship2 olpc2-trial3 olpc2-trial3 olpc2-trial3 olpc2-update1 olpc2-update1 olpc2-update1 通过指定 —name 参数,可以得到它的列表:
[root@localhost ~]# koji list-targets --name dist-f10 Name Buildroot Destination
dist-f10 dist-f10-build dist-f10 上面结果告诉我们,对于 dist-f10 这个 target 的编译将会使用 dist-f10-build 这个 tag 中的包作为 buildroot ,将编译后的包标记到 dist-f10 这个 tag 中。
使用下面命令可以得到所有 tag 的列表:
[root@localhost ~]# koji list-tags ... dist-f10 dist-f10-build dist-f10-kernel dist-f10-override dist-f10-updates dist-f10-updates-candidate dist-f10-updates-testing ... f10-alpha f10-beta f10-final ... Package lists
上面提到,每个 tag 都有自己的 packages 列表,这些包可以放在这个 tag 里。 使用 list-pkgs 命令可以看到 tag 中的包列表:
[root@localhost ~]# koji list-pkgs --tag=gtes-11 Package Tag Extra Arches Owner
----------------------- ---------------- ---------------
CMap gtes-11 jianlee ElectricFence gtes-11 jianlee GConf2 gtes-11 jianlee GeoIP gtes-11 jianlee ImageMagick gtes-11 jianlee MAKEDEV gtes-11 jianlee MySQL-python gtes-11 jianlee ... Latest Builds
Documentation ( 文件 )
通过查看koji的help手册获得帮主信息。
koji help # 输出匿名用户可以使用的命令的帮助信息 koji build help # 输出 build 命令的帮助信息 koji help --admin # 输出管理员可以使用的命令(即所有命令)帮助信息 创建kojiserver
基础知识
Basic understanding of SSL and authentication via certificates and/or Kerberos credentials Basic knowledge about creating a database in PostgreSQL and importing a schema Working with psql Basic knowledge about Apache configuration Basic knowledge about yum/createrepo/mock - else you'll not be able to debug problems! Basic knowledge about using command line Basic knowledge about RPM building Simple usage of the Koji client 需要的软件包
服务端 (koji-hub/koji-web)
httpd mod_ssl postgresql-server mod_python (= 3.3.1 for Kerberos authentication) 客户端(koji-builder)
mock setarch (for some archs you'll require a patched version) rpm-build createrepo 磁盘空间要求
KojiDir目录需要大量空间,在kojihub.conf里配置。如果koji使用mock作为后端 编译工具。用户会发现/var/lib/mock非常大。用户需要在kojid.conf中调整 mock的默认编译目录。
koji认证
Koji主要支持 Kerberos 和 SSL Certificate 认证。对于基本的命令行访问,通 常的用户名/密码组合也可以。但是,kojiweb不支持用户名/密码认证。因此,只 有 Kerberos 或 SSL Certificate 其中一种认证建立,kojiweb才会工作
创建 SSL Certificate 认证
Certificate generation
拷贝下面的 ssl.cnf 文件到 /etc/pki/koji/ssl.cnf 。修改一些信息为自己的。
HOME = . RANDFILE = .rand
[ca] default_ca = ca_default
[ca_default] dir = . certs = $dir/certs crl_dir = $dir/crl database = $dir/index.txt new_certs_dir = $dir/newcerts certificate = $dir/%s_ca_cert.pem private_key = $dir/private/%s_ca_key.pem serial = $dir/serial crl = $dir/crl.pem x509_extensions = usr_cert name_opt = ca_default cert_opt = ca_default default_days = 3650 default_crl_days = 30 default_md = md5 preserve = no policy = policy_match
[policy_match] countryName = match stateOrProvinceName = match organizationName = match organizationalUnitName = optional commonName = supplied emailAddress = optional
[req] default_bits = 1024 default_keyfile = privkey.pem distinguished_name = req_distinguished_name attributes = req_attributes x509_extensions = v3_ca # The extentions to add to the self signed cert string_mask = MASK:0x2002
[req_distinguished_name] countryName = Country Name (2 letter code) countryName_default = CN countryName_min = 2 countryName_max = 2 stateOrProvinceName = State or Province Name (full name) stateOrProvinceName_default = BeiJing localityName = Locality Name (eg, city) localityName_default = Beijing 0.organizationName = Organization Name (eg, company) 0.organizationName_default = TurboLinux organizationalUnitName = Organizational Unit Name (eg, section) commonName = Common Name (eg, your name or your server\'s hostname) commonName_default = koji commonName_max = 64 emailAddress = Email Address emailAddress_default = jian.li@turbolinux.com.cn emailAddress_max = 64
[req_attributes] challengePassword = A challenge password challengePassword_min = 4 challengePassword_max = 20 unstructuredName = An optional company name
[usr_cert] basicConstraints = CA:FALSE nsComment = "OpenSSL Generated Certificate" subjectKeyIdentifier = hash authorityKeyIdentifier = keyid,issuer:always
[v3_ca] subjectKeyIdentifier = hash authorityKeyIdentifier = keyid:always,issuer:always basicConstraints = CA:true 创建 CA
在Koji的其他部分,clientca.crt 和 serverca.crt,都是指用下面命令产生的 koji_ca_cert.key 文件:
cd /etc/pki/koji/ mkdir {certs,private} touch index.txt echo 01 > serial caname=koji openssl genrsa -out private/${caname}_ca_cert.key 2048 openssl req -config ssl.cnf -new -x509 -days 3650 -key private/${caname}_ca_cert.key \ -out ${caname}_ca_cert.crt -extensions v3_ca 创建其他部分的 cert 和 kojiadmin 账户的 cert
for user in kojira kojiweb kojihub kojibuilder{1..5} kojiadmin; do openssl genrsa -out certs/${user}.key 2048 openssl req -config ssl.cnf -new -nodes -out certs/${user}.csr -key certs/${user}.key openssl ca -config ssl.cnf -keyfile private/${caname}_ca_cert.key -cert ${caname}_ca_cert.crt \ -out certs/${user}.crt -outdir certs -infiles certs/${user}.csr cat certs/${user}.crt certs/${user}.key > ${user}.pem done 其中/usr/share/doc/koji-1.3.1/docs/schema.sql文件中的sql指令创建了下面 这些基本用户
-- Some basic perms INSERT INTO permissions (name) VALUES ('admin'); INSERT INTO permissions (name) VALUES ('build'); INSERT INTO permissions (name) VALUES ('repo'); 创建 PKCS12 user certificate (for web browser)
如果用户使用web访问kojihub,需要为用户另外生成一个cert。
openssl pkcs12 -export -inkey certs/${user}.key -in certs/${user}.crt -CAfile ${caname}_ca_cert.crt \ -out certs/${user}_browser_cert.p12
> 为 kojiadmin 拷贝认证文件
上面设置了账户为admin,因为数据库初始化的时候管理员账户就是这个名字!可 以自己修改
mkdir ~/.koji cp -pv /etc/pki/koji/kojiadmin.pem ~/.koji/client.crt cp -pv /etc/pki/koji/koji_ca_cert.crt ~/.koji/clientca.crt cp -pv /etc/pki/koji/koji_ca_cert.crt ~/.koji/serverca.crt 配置 koji 命令行程序
koji 命令行程序默认使用 /etc/koji.conf 配置文件,但是每个用户的 ~/.koji/config 文件会覆盖全局文件的设置。
PostgreSQL Server 配置
/var/lib/pgsql/data/pg_hba.conf /var/lib/pgsql/data/postgresql.conf 初始化数据库并启动postgresql
GTES 11.2 第一次启动 postgresql 时候会自动初始化数据库:
[root@dev koji]# /etc/init.d/postgresql start 正在初始化数据库: [确定] 启动 postgresql 服务: [确定] 创建系统koji账号并清空密码
[root@dev koji]# useradd koji [root@dev koji]# passwd -d koji Removing password for user koji. passwd: Success 创建koji数据库用户并初始化koji数据库
[root@dev koji]# su - postgres -bash-3.2$ createuser koji Shall the new role be a superuser? (y/n) n Shall the new role be allowed to create databases? (y/n) n Shall the new role be allowed to create more new roles? (y/n) n CREATE ROLE -bash-3.2$ createdb -O koji koji CREATE DATABASE -bash-3.2$ logout [root@dev koji]# su - koji [koji@dev ~]$ psql koji koji < /usr/share/doc/koji-1.3.1/docs/schema.sql # 这里的文件地址随版本号可能有变 [koji@dev ~]$ exit 设置koji用户访问postgresql数据库权限
本例中,kojiweb和kojihub都是在本地localhost上运行。在 /var/lib/pgsql/data/pg_hba.conf文件中增加下面一行:
host koji koji 127.0.0.1/32 trust 应用改变:
[root@dev koji]# su - postgres -bash-3.2$ pg_ctl reload postmaster 发出信号 -bash-3.2$ exit 创建管理员账号 重要
这里最重要,管理员账号要手动创建,其他用户可以用管理员权限创建,如果使 用username/password验证方式访问数据库,那么管理员创建的其他用户的密码需 要手动设置。
[root@dev koji]# su - koji [koji@dev ~]$ psql koji=> insert into users (name, password, status, usertype) values ('kojiadmin', 'turbolinux', 0, 1); INSERT 0 1 koji=> select * from users; # 这里要注意!例子中 id=1
id | name | password | status | usertype | krb_principal
+-----------+------------+--------+----------+---------------
1 | kojiadmin | turbolinux | 0 | 1 |
(1 行) koji=> insert into user_perms (user_id, perm_id) values (1, 1); # user_id字段就是上面看到的值--1 INSERT 0 1 Koji Hub 配置
/etc/httpd/conf/httpd.conf /etc/httpd/conf.d/kojihub.conf /etc/httpd/conf.d/ssl.conf (when using ssl auth) 修改apache的性能(留作疑问?)
<IfModule prefork.c> ... MaxRequestsPerChild 100 </IfModule> <IfModule worker.c> ... MaxRequestsPerChild 100 </IfModule> 配置 /etc/httpd/conf.d/kojihub.conf
通常这个文件中包含这样一行:
PythonOption ConfigFile /etc/koji-hub/hub.conf
如果使用 ssl 认证,kojihub.conf文件中设置:
<Location /kojihub>
SSLOptions +StdEnvVars
</Location> 我们可以配置 /etc/koji-hub/hub.conf 文件,下面值设置要注意(本例都使用ssl认证方式):
DBName = koji DBUser = koji DBHost = localhost DBPass = 密码字符串 KojiDir = /mnt/koji ... DNUsernameComponent = CN ProxyDNs = /C=CN/ST=BeiJing/L=Beijing/O=TurboLinux/CN=koji/emailAddress=jian.li@turbolinux.com.cn ... KojiWebURL = http://172.16.70.48/koji 其中 ProxyDNs 和 kojiweb 认证文件的 DirName 字段一样。
其中密码是这样设置的:
[root@dev koji]# su - postgres psql postgres=# ALTER USER koji with password '密码字符串' 配置 /etc/httpd/conf.d/ssl.conf
SSLCertificateFile /etc/pki/koji/certs/kojihub.crt SSLCertificateKeyFile /etc/pki/koji/certs/kojihub.key SSLCertificateChainFile /etc/pki/koji/koji_ca_cert.crt SSLCACertificateFile /etc/pki/koji/koji_ca_cert.crt SSLVerifyClient require SSLVerifyDepth 10 设置 SELinux
如果运行了 SELinux,那么要容许 apache 访问 sql:
[root@dev koji]# sestatus SELinux status: enabled SELinuxfs mount: /selinux Current mode: enforcing Mode from config file: enforcing Policy version: 21 Policy from config file: targeted [root@dev koji]# setsebool -P httpd_can_network_connect_db 1 文件系统设置
例子设置了 KojiDir 为 /mnt/koji
cd /mnt mkdir koji cd koji mkdir {packages,repos,work,scratch} chown apache.apache * 创建kojira用户
现在重启 httpd ,kojihub应该可以通过 koji 命令行程序访问了。如果上面配 置正确,用 kojiadmin 的认证权限可以创建用户和设置用户权限了:
[root@dev turbo]# koji add-user kojira Added user kojira (2) [root@dev turbo]# koji grant-permission repo kojira Koji Web 配置
/etc/httpd/conf.d/kojiweb.conf /etc/httpd/conf.d/ssl.conf kojiweb.conf 配置
以ssl认证为例,
PythonOption KojiHubURL http://172.16.70.48/kojihub PythonOption KojiPackagesURL http://172.16.70.48/mnt/koji/packages
- PythonOption WebPrincipal koji/web@EXAMPLE.COM
- PythonOption WebKeytab /etc/httpd.keytab
- PythonOption WebCCache /var/tmp/kojiweb.ccache
PythonOption WebCert /etc/pki/koji/kojiweb.pem PythonOption ClientCA /etc/pki/koji/koji_ca_cert.crt PythonOption KojiHubCA /etc/pki/koji/koji_ca_cert.crt
... <Location /koji/login>
SSLOptions +StdEnvVars
</Location> Koji builder
/etc/kojid/kojid.conf - Koji Daemon Configuration /etc/sysconfig/kojid - Koji Daemon Switches 例如我的 kojibuilder1 机器配置:
[root@localhost ~]# sed -e '/^;/d;/^$/d' /etc/kojid/kojid.conf [kojid] sleeptime=15 maxjobs=10 minspace=8192 topdir=/mnt/koji workdir=/tmp/koji mockdir=/var/lib/mock mockuser=kojibuilder vendor=TurboLinux packager=RD distribution=TurboLinux mockhost=turbo-linux-gnu server=http://172.16.70.48/kojihub pkgurl=http://172.16.70.48/packages smtphost=localhost from_addr=TurboLinux Build System <jian.li@turbolinux.com.cn> cert = /etc/kojid/kojibuilder1.pem ca = /etc/kojid/koji_ca_cert.crt serverca = /etc/kojid/koji_ca_cert.crt 启动 kojid
[root@localhost ~]# koji add-host kojibuilder1 i386 x86_64 kojibuilder1 added: id 1 [root@localhost ~]# koji list-hosts Hostname Enb Rdy Load/Cap Arches Last Update kojibuilder1 Y N 0.0/2.0 i386,x86_64 - [root@localhost ~]# /etc/init.d/kojid start 启动 kojid: [确定] [root@localhost ~]# koji list-hosts Hostname Enb Rdy Load/Cap Arches Last Update kojibuilder1 Y Y 0.0/2.0 i386,x86_64 2009-05-19 23:50:24 添加 kojibuilder1 到 createrepo channel
- koji add-host-to-channel kojibuilder1 createrepo
注意 capacity
默认权值是 2 ,可以通过pgsql手动修改:
[koji@localhost ~]$ psql koji koji=> select (id, name, capacity) from host;
row
(1,kojibuilder1,2)
(1 行) koji=> update host set capacity = 16 where id = 1; UPDATE 1 koji=> select (id, name, capacity) from host;
row
(1,kojibuilder1,16)
(1 行) kojira 配置
/etc/kojira/kojira.conf - Kojira Daemon Configuration /etc/sysconfig/kojira - Kojira Daemon Switches [root@localhost ~]# sed -e '/^;/d;/^$/d' /etc/kojira/kojira.conf [kojira] server=http://172.16.70.48/kojihub topdir=/mnt/koji logfile=/var/log/kojira.log with_src=no cert = /etc/kojira/kojira.pem ca = /etc/kojira/koji_ca_cert.crt serverca = /etc/kojira/koji_ca_cert.crt 如果上面添加 kojira 用户的命令没有执行,现在需要做了!
koji add-user kojira koji grant-permission repo kojira 启动 kojira
初始化 koji build system 环境!
导入所有的SRPMS和RPMS
koji最好所有包放在同一个分区上面,这样快。不然每个包koji都要用自己的方式上传
koji import --link mithras/SRPMS/* mithras/RPMS/i386/* mithras/RPMS/i686/* mithras/RPMS/ia64/* mithras/RPMS/noarch/* mithras/RPMS/x86_64/* 创建新的tag
koji add-tag gtes11.2 给导入的包标记上 tag
koji list-pkgs --quiet | xargs koji add-pkg --owner kojiadmin gtes11.2 koji list-untagged | xargs -n 1 koji call tagBuildBypass gtes11.2 最后一不调用 tagBuildBypass 而不是用 koji tag-pkg ,在 这里大量处理的时候快速。
创建一个 build tag
koji add-tag --parent gtes11.2 --arches "i386 x86_64 ia64" gtes11.2-build 创建一个 build target
koji add-target gtes11.2 gtes11.2-build 创建一个 build group
koji add-group gtes11.2-build build 添加 pkg 到 build group
koji add-group-pkg dist-foo-build build pkg1 pkg2 pkg3 ... gtes11.2项目这样创建 build group:
koji add-group-pkg gtes11.2-build build bash bzip2 coreutils cpio dev diffutils \
e2fsprogs file findutils gawk gcc gcc-c++ grep gzip info kernel-headers make \ module-init-tools patch rpm rpm-build sed shadow-utils tar turbo-rpm-config \ turbolinux-release udev unzip util-linux which
现在可以等待 creatrepo 任务完成,然后使用编译系统了。
常用命令
创建用户认证文件
cd /etc/pki/koji/ caname=koji for user in jianlee holmesw; do openssl genrsa -out certs/${user}.key 2048 openssl req -config ssl.cnf -new -nodes -out certs/${user}.csr -key certs/${user}.key openssl ca -config ssl.cnf -keyfile private/${caname}_ca_cert.key -cert ${caname}_ca_cert.crt \ -out certs/${user}.crt -outdir certs -infiles certs/${user}.csr cat certs/${user}.crt certs/${user}.key > ${user}.pem done 创建 web 认证 (PKCS12 user certificate)
user = jianlee openssl pkcs12 -export -inkey certs/${user}.key -in certs/${user}.crt -CAfile ${caname}_ca_cert.crt \ -out certs/${user}_browser_cert.p12 系统管理
创建 tag
创建 tag gtes11.3,继承 gtes11.2 的所有包
koji add-tag --parent=gtes11.2 --arches="i386 x86_64 ia64" gtes11.3 设置用户的权限
koji 从 1.3.1 开始使用 policy 控制用户的权限(admin除外),在 /etc/koji-hub/hub.conf 中添加设置:
[policy] build_from_srpm =
tag gtes11.2 :: allow
tag gtes11.3 :: allow
has_perm build :: allow
all :: deny
使用管理账户添加用户权限:
koji grant-permission build jianlee 上面的 build 和 admin 及 repo 都是初始化 koji 数据库的时候创建的基本权 限,在初始化数据库脚本有(koji 1.3.1):
96 -- Some basic perms
97 INSERT INTO permissions (name) VALUES ('admin');
98 INSERT INTO permissions (name) VALUES ('build');
99 INSERT INTO permissions (name) VALUES ('repo');
给jianlee添加build权限后,数据库中几个表的内容如下:
koji=> SELECT * from permissions;
id | name
+-------
1 | admin 2 | build 3 | repo
(3 行)
koji=> SELECT * from user_perms ;
user_id | perm_id | create_event | revoke_event | active
+---------+--------------+--------------+--------
1 | 1 | 1 | | t
2 | 3 | 2 | | t
12 | 2 | 4512 | | t
(3 行)
koji=> SELECT * from users;
id | name | password | status | usertype | krb_principal
+--------------+------------+--------+----------+---------------
1 | turbo | turbolinux | 0 | 1 | 2 | kojira | | 0 | 0 | 5 | kojibuilder2 | | 0 | 1 | 9 | kojibuilder3 | | 0 | 1 | 12 | jianlee | | 0 | 0 | 13 | antonf | | 0 | 0 |
(6 行) 问题解决
删除数据库里面的包
delete from changelogs where build_id in (select id from build where pkg_id in (select id from package where name = 'httpd')); delete from tag_listing where build_id in (select id from build where pkg_id in (select id from package where name = 'httpd')); delete from rpmsigs where rpm_id in (select id from rpminfo where build_id in (select id from build where pkg_id in (select id from package where name = 'httpd'))); delete from rpmdeps where rpm_id in (select id from rpminfo where build_id in (select id from build where pkg_id in (select id from package where name = 'httpd'))); delete from rpmhttpds where rpm_id in (select id from rpminfo where build_id in (select id from build where pkg_id in (select id from package where name = 'httpd'))); delete from buildroot_listing where rpm_id in (select id from rpminfo where build_id in (select id from build where pkg_id in (select id from package where name = 'httpd'))); delete from rpminfo where build_id in (select id from build where pkg_id in (select id from package where name = 'httpd')); delete from build where pkg_id = (select id from package where name = 'httpd'); delete from tag_packages where package_id = (select id from package where name = 'httpd'); delete from package where name = 'httpd'; SELinux 问题
强烈推荐开启 SELinux ,我的 KojiDir = /data/koji
[root@yy-132-26-a8 data]# ls -Z /data/ -d drwxr-xr-x root root system_u:object_r:httpd_sys_content_t /data/ [root@yy-132-26-a8 data]# ls -Z koji drwxr-xr-x apache apache user_u:object_r:httpd_sys_content_t packages drwxr-xr-x apache apache user_u:object_r:httpd_sys_content_t repos drwxr-xr-x apache apache user_u:object_r:httpd_sys_content_t scratch drwxr-xr-x apache apache user_u:object_r:httpd_sys_content_t work [root@yy-132-26-a8 data]# pwd /data Web 访问 Koji 的 pkgs 目录
Alias /mnt/koji/packages /mnt/koji/packages Alias /packages /mnt/koji/packages <Directory "/mnt/koji/packages">
Options all
</Directory> Web 登录
生成一个 p12 key
由管理员在koji服务器 /etc/pki/koji 目录下用下面命令生成一个 ${user}_browser_cert.p12
openssl pkcs12 -export -inkey certs/${user}.key -in certs/${user}.crt -CAfile ${caname}_ca_cert.crt \ -out certs/${user}_browser_cert.p12 拷贝需要的文件
${user}.pem ---> ~/.fedora.cert ${caname}_ca_cert.crt ---> ~/.fedora-server-ca.cert 导入 ${user}_brower_cert.p12 到浏览器(firefox,opera等)
以 Firefox 为例,以此点击“编辑” -> “首选项 -> 高级 -> 加密 -> 查看证书 -> 您的证书 -> 导入 。选择证书 ${user}_browser_cert.p12,证书的密码是创 建时候设置的。
邮件通知
koji可以提供邮件通知,在 builder/kojid 里面有下面发信模块:
message = self.message_templ % locals()
# ensure message is in UTF-8
message = message.encode('utf-8')
server = smtplib.SMTP(options.smtphost)
#server.set_debuglevel(True)
server.sendmail(from_addr, recipients, message)
server.quit()
这个模块采用直接发送方式,不需要通过验证,都是收件人必须在smtp服务器上存在。在 builder/kojid.conf 中有配置选项:
smtphost=turbolinux.com.cn # 这里是smtp服务器地址,只要开了110端口就行,不需要验证。 from_addr=Turbolinux Build System <jian.li@turbolinux.com.cn> # 为了方便其他人联系管理员,这里设置成管理员地址。 在 hub/hub.conf 中有下面选项:
EmailDomain = turbolinux.com.cn # 收件人的域名,不指定,通常发邮件到 user@None!你不想这样吧?不过可以修改上面的数据库中内容达到目的。 NotifyOnSuccess = True # 这个控制在软件包编译成功的时候是否发送邮件。 koji=> SELECT * from build_notifications;
id | user_id | package_id | tag_id | success_only | email
+---------+------------+--------+--------------+--------------
1 | 1 | | | f | turbo@None 2 | 12 | | | f | jianlee@None
(2 行) 更换koji服务器IP,yun还是指向以前IP的问题
方法一:修改 /usr/sbin/kojid
更换服务器IP后,需要修改 koji.conf kojid.conf kojihub.conf kojiweb.conf 等等配置,但是最后需要注意的一点是:koji默认执行的 createrepo 命令参数是(查看 createrepo.log 文件)
$ /usr/bin/createrepo -vd -o /tmp/koji/tasks/265/265/repo \
-i /mnt/koji/repos/moblin2-build/47/i386/pkglist \
-u http://172.16.70.33/packages \
-g /mnt/koji/repos/moblin2-build/47/groups/comps.xml \
--update --skip-stat /mnt/koji/packages/
上面的显示最后两个参数是 "—update —skip-stat" ,这样生成的 repo 信息库基于以前的,现在我还不清楚 repo 信息库的格式和存储的具体信息,但是去掉这两个参数能解决问题。
在 /usr/sbin/kojid 里面注释调下面三行:
2584 #cmd.append('--update') 2585 #if options.createrepo_skip_stat: 2586 # cmd.append('--skip-stat') 再重新使用 "koji regen-repo moblin-build2" 就可以重新从头开始 生成 repo库。最后测试是否能顺利使用。当这一切都过去后,把上面修改的行恢 复,这样下次 createrepo 会省时省力。
方法二: 修改数据库(简单,推荐)
update repo set state = 2 where state in (0, 1); from koji/__init__.py: REPO_STATES = Enum((
'INIT', 'READY', 'EXPIRED', 'DELETED', 'PROBLEM',
))
So 0 = INIT, 1 = READY, 2 = EXPIRED, 3 = DELETED 有 Extra Arches 的包(比如kernel)
通常我们定义一个 build target 为 i386/i586/i686,x86_64,ia64,.. 的 arches。但是有些包(如kernel,glibc)同时需要编译 i386/i586,i686 架构。 这时候就需要 Extra Arches 了。给一个包增加一个 Extra Arch 同给包设置 Arch 一样:
koji set-pkg-arches i686 gtes11.3 kernel 下面是 gtes11.2 增加实例:
koji set-pkg-arches i686 gtes11.2 kernel glibc ocfs2 openssl kvm-kmod gnbd-kmod 删除一个build
先要untag所有依赖,比如很多tag是从其他的tag继承过来,要从继承时候就有此 build处untag。
[root@build ~]# koji untag-pkg tms2.0 system-config-language-1.3.2-6.1.moblin2 [root@build ~]# koji call deleteBuild system-config-language-1.3.2-6.1.moblin2 tms2.0 GenericError: Cannot delete build, tagged: [{'id': 11, 'name': 'moblin2-devel'}] [root@build ~]# koji untag-pkg moblin2-devel system-config-language-1.3.2-6.1.moblin2 [root@build ~]# koji call deleteBuild system-config-language-1.3.2-6.1.moblin2 tms2.0 True 关于管理员权限
在使用下面命令之后,我们就自动创建了三个内部角色,其中一个重要角色就是 ADMIN。
psql koji koji < /usr/share/doc/koji-1.3.1/docs/schema.sql 进入数据库:
- su - koji
$ psql 查看当前权限角色:
koji=> SELECT * from permissions;
id | name
+-------
1 | admin 2 | build 3 | repo
(3 行) 我们看到上面 admin 角色的 id 是 1 , 请记住,如果要手动创建管理员权限的 用户时就要用这个角色 id !(koji系统搭建过程中第一个管理员权限就是手动 创建的)
现在查看当前用户权限:
koji=> SELECT * from user_perms ;
user_id | perm_id | create_event | revoke_event | active
+---------+--------------+--------------+--------
1 | 1 | 2 | | t
3 | 3 | 3 | | t
(2 行) 上面显示 user_id = 1 的用户拥有权限 perm_id = 1 ,即这个用户有 admin 权 限。我们再查看一下 user_id = 1 的用户名是什么:
koji=> SELECT * from users;
id | name | password | status | usertype | krb_principal
+---------------+----------+--------+----------+---------------
1 | admin | | 0 | 1 | 2 | admin-account | | 0 | 0 | 3 | kojira | | 0 | 0 | 4 | jianlee | | 0 | 0 | 6 | kojibuilder1 | | 0 | 1 | 7 | kojibuilder2 | | 0 | 1 | 8 | kojibuilder3 | | 0 | 1 | 9 | holmesw | | 0 | 0 | 10 | lijian | | 0 | 0 |
(9 行)
koji=> 哦,在我的系统 user_id = 1 的用户名是 "admin" 。
注意 , 角色名和用户名不是一回事,可以同名!
kojid 问题:常见编译服务器错误
如果我们第一次创建一个 kojibuilder 出现下面错误:
Traceback (most recent call last):
File "/usr/sbin/kojid", line 1275, in runTask response = (handler.run(),) File "/usr/sbin/kojid", line 1351, in run return self.handler(*self.params,**self.opts) File "/usr/sbin/kojid", line 2009, in handler broot.init() File "/usr/sbin/kojid", line 467, in init rv = self.mock(['--init']) File "/usr/sbin/kojid", line 389, in mock status = os.waitpid(pid, os.WNOHANG)
OSError: [Errno 10] No child processes 有可能是目录权限或 kojibuilder 用户没有创建的原因:
- ll /var/lib/mock/ -d
drwxrwsr-x 2 root mock 4096 09-10 09:55 /var/lib/mock/
- grep koji /etc/passwd
kojibuilder:x:101:107::/builddir:/bin/bash
- grep koji /etc/group
mock:x:110:kojibuilder kojibuilder:x:107: chroot时区和系统时区不对应导致changelog日期提前12小时
默认的chroot环境使用 EDT (美国东部时区),通常我们的服务器使用 Asia/Shanghai 时区。这样编译后的包用 "rpm -qpi —changelog ***.rpm" 查 看的时间提前12小时(没有修改 spec)文件。
我没有深入研究,只是在 mock 创建 chroot 环境的最后面拷贝 Asia/Shanghai 到 /ect/localtime。在文件 /usr/lib/python2.4/site-packages/mock/backend.py 里(下面的第581行是我 添加的):
577 self.doChroot(self.useradd % dets, shell=True) 578 self.doChroot( 579 ["perl", "-p", "-i", "-e", 's/^(%s:)!!/$1/;' % self.chrootuser, "/etc/passwd"], 580 shell=False, raiseExc=True) 581 self.doChroot(['/bin/cp', '-v', '/usr/share/zoneinfo/Asia/Shanghai', '/etc/localtime'], shell=False)