(Edited due to recent watcher/event rethinking) |
|||
| Line 4: | Line 4: | ||
[[Image:autoqa_architecture.png|600px]] | [[Image:autoqa_architecture.png|600px]] | ||
== | == Events and watchers == | ||
AutoQA defines "hooks" for events that we are interested in. A hook basically consists of: | <!-- AutoQA defines "hooks" for events that we are interested in. A hook basically consists of: | ||
* A definition of the event we're watching for | * A definition of the event we're watching for | ||
* A Watcher program to monitor for the event and gather arguments needed for the tests | * A Watcher program to monitor for the event and gather arguments needed for the tests | ||
* Code to handle the arguments passed from the watcher | * Code to handle the arguments passed from the watcher | ||
* A list of tests to run when the hook is triggered | * A list of tests to run when the hook is triggered | ||
* Template files for writing new tests for this hook | * Template files for writing new tests for this hook --> | ||
AutoQA defines "watchers" that look for various "events" happening within the Fedora development/build process. Basically watchers are programs that monitor for the events and gather arguments needed for the tests. Events are defined separately from watchers as a single watcher can check for multiple events. A code to handle the arguments passed from the watcher is part of each event. | |||
=== Defining Events === | === Defining Events === | ||
For AutoQA to respond to an event, someone needs to create | For AutoQA to respond to an event, someone needs to create or modify existing watcher that will respond to such an event. The first step is, obviously, to define the event itself. | ||
For example, the <code>post-repo-update</code> | For example, the <code>post-repo-update</code> event is triggered whenever <code>yum-repo</code> watcher determines that a Fedora repo is updated. The repo update is the event, and, obviously, any <code>post-repo-update</code> test needs to know the URL of the repo that was just updated. (This is an example of a ''required'' argument.) Certain repos can't be used properly without other "parent" repos (for example, the Fedora 11 <code>updates</code> repo isn't useful without also knowing the address of the main Fedora 11 repo). So a list of "parent repos" is an ''optional'' argument to the tests. | ||
=== Watchers === | === Watchers === | ||
This is a program that watches for the event and launches the autoqa harness when the event occurs. The Watcher is responsible for filling in all the optional arguments for the event and passing that information along to autoqa. Typically watchers are run periodically through cron. | |||
=== Test arguments === | === Test arguments === | ||
| Line 27: | Line 29: | ||
The autoqa test launcher needs to know how to process the arguments gathered by the watcher | The autoqa test launcher needs to know how to process the arguments gathered by the watcher | ||
More detailed information about implementing new | More detailed information about implementing new events can be found in [[Writing AutoQA Hooks]]. | ||
== The autoqa Harness == | == The autoqa Harness == | ||
Revision as of 14:13, 28 March 2011
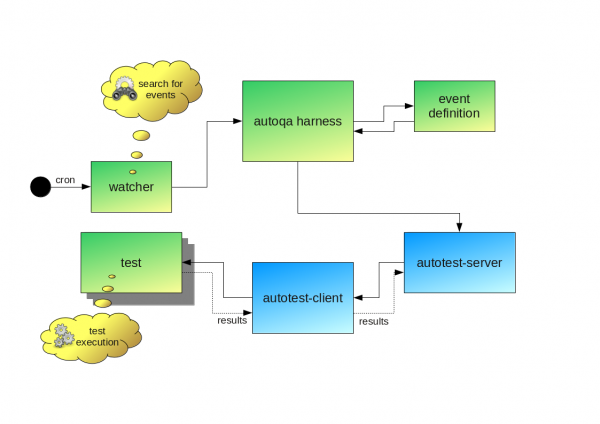
This document describes how AutoQA is structured internally.
Quick look
Events and watchers
AutoQA defines "watchers" that look for various "events" happening within the Fedora development/build process. Basically watchers are programs that monitor for the events and gather arguments needed for the tests. Events are defined separately from watchers as a single watcher can check for multiple events. A code to handle the arguments passed from the watcher is part of each event.
Defining Events
For AutoQA to respond to an event, someone needs to create or modify existing watcher that will respond to such an event. The first step is, obviously, to define the event itself.
For example, the post-repo-update event is triggered whenever yum-repo watcher determines that a Fedora repo is updated. The repo update is the event, and, obviously, any post-repo-update test needs to know the URL of the repo that was just updated. (This is an example of a required argument.) Certain repos can't be used properly without other "parent" repos (for example, the Fedora 11 updates repo isn't useful without also knowing the address of the main Fedora 11 repo). So a list of "parent repos" is an optional argument to the tests.
Watchers
This is a program that watches for the event and launches the autoqa harness when the event occurs. The Watcher is responsible for filling in all the optional arguments for the event and passing that information along to autoqa. Typically watchers are run periodically through cron.
Test arguments
The autoqa test launcher needs to know how to process the arguments gathered by the watcher
More detailed information about implementing new events can be found in Writing AutoQA Hooks.
The autoqa Harness
The autoqa harness is launched by the watchers in response to an event. It's basically just a python script, /usr/bin/autoqa, which handles the arguments passed by the watcher and schedules the appropriate tests to be run in autotest.
Autotest
Autotest is "a framework for automated testing". It handles scheduling test jobs from the job queue, putting the test code onto the appropriate test machine, running the test, and gathering the test results for later examination. For more information see Autotest.
Tests
AutoQA tests consist of some test metadata, some setup and test reporting code, and the test itself - which may be a pre-existing test or a new test written specifically for AutoQA.
The test results are reported back to the Autotest system and can be examined through its web interface. Tests can also opt to report their results in other ways - commonly by sending email to the autoqa-results mailing list.
For more detailed information about AutoQA tests, see Writing AutoQA Tests.