From Fedora Project Wiki
(adjust associated_release_criterion template invocation) |
(Updated PXE Server config pointer to F20 docs) |
||
| Line 9: | Line 9: | ||
<li>''Option 1:'' Set up a PXE server. | <li>''Option 1:'' Set up a PXE server. | ||
<ul> | <ul> | ||
<li>This is not an easy task and requires some administrator knowledge. You can read the [http://docs.fedoraproject.org/en-US/Fedora/ | <li>This is not an easy task and requires some administrator knowledge. You can read the [http://docs.fedoraproject.org/en-US/Fedora/20/html/Installation_Guide/s1-netboot-pxe-config.html appropriate section in the Installation guide for Fedora 20].</li> | ||
<li>The custom pxelinux config file can look like this: | <li>The custom pxelinux config file can look like this: | ||
{{#tag:pre|DEFAULT vesamenu.c32 | {{#tag:pre|DEFAULT vesamenu.c32 | ||
Revision as of 14:51, 13 September 2014
Description
This is to verify that it is possible to boot Anaconda and install the system by direct kernel+initrd boot. That can be achieved either by using PXE boot or by booting the kernel directly in a virtual machine.
Setup
- You will need
vmlinuzandinitrd.imgfiles. Those are located in the(arch)/os/images/pxebootdirectory of the tree for the Fedora compose you wish to test. - You will need a remote location containing Anaconda's
LiveOS/directory (containing the installer) and optionally also a package repository. Development composes are usually available at dl.fedoraproject.org/pub/alt/stage/ (doesn't contain package repository). If you have a local mirror, you can make it accessible over any protocol supported by inst.repo boot option. - Option 1: Set up a PXE server.
- This is not an easy task and requires some administrator knowledge. You can read the appropriate section in the Installation guide for Fedora 20.
- The custom pxelinux config file can look like this:
DEFAULT vesamenu.c32 LABEL Fedora 42-Alpha-RC1 x86_64 KERNEL vmlinuz INITRD initrd.img APPEND inst.repo=http://dl.fedoraproject.org/pub/alt/stage/42-Alpha-RC1/Fedora/x86_64/os/
- Option 2: Boot kernel directly in a virtual machine.
- Prepare a virtual machine that can boot kernel+initrd pair directly, e.g. using
 virt-manager
virt-manager
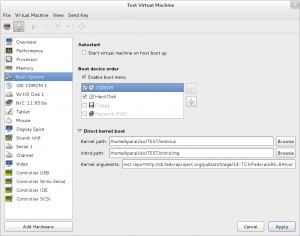
- Prepare a virtual machine that can boot kernel+initrd pair directly, e.g. using
How to test
- Boot the system via PXE, or using a virtual machine with appropriate inst.repo boot argument (it has to point to the same compose you used for retrieving
vmlinuzandinitrd.img). - Proceed with installation.
Expected Results
- The system boots (using PXE or direct kernel boot in a virtual machine) and it downloads anaconda installer from the specified remote location.
- The installer starts correctly.
- If the remote location contains a yum repository, the said repository is used for installation. This can be checked by examining the
/tmp/packaging.logfile. Example output:09:34:37,295 DEBUG packaging: adding yum repo anaconda with baseurl http://download.fedoraproject.org/pub/fedora/linux/development/42/x86_64/os/ and mirrorlist None 09:34:37,313 DEBUG packaging: disabling repo fedora 09:34:37,313 DEBUG packaging: disabling repo updates-testing 09:34:37,314 DEBUG packaging: disabling repo updates
- The installation completes and the new system initiates boot properly

