m (reshuffle some bits with small finetuning) |
(Why are there no new mainline snapshots on some days) |
||
| Line 116: | Line 116: | ||
That being said: in very rare situations we might include a patch to fix build problems. That normally only happens for mainline builds; those fixes often head upstream quickly and hence vanish from the vanilla packages pretty soon again. | That being said: in very rare situations we might include a patch to fix build problems. That normally only happens for mainline builds; those fixes often head upstream quickly and hence vanish from the vanilla packages pretty soon again. | ||
== Why are there no new mainline snapshots on some days? == | |||
Usually it's because nothing changed in mainline, so there was no reason to build new packages; this most commonly happens on Tuesdays and Wednesdays (UTC) during the stabilization phase. | |||
== Why so many repos? This looks stupid and over-engineered! == | == Why so many repos? This looks stupid and over-engineered! == | ||
Revision as of 04:47, 17 April 2024
Frequently asked questions about the kernel vanilla repositories for Fedora.
FAQ for users
What is the goal of these repositories?
There are two main goals:
- Help upstream Linux development, which in the end benefits Fedora as well.
- Make it easy for users of Fedora Linux to check if a kernel bug they face occurs with the latest upstream versions as well.
To explain in more details:
- With the packages from the @kernel-vanilla/mainline repository it for example is quite easy to test the code that down the road will land in Fedora Linux. In other words: the repository allows people to find, report, and eliminate bugs to prevent them ever hitting a Fedora release. The packages also make it easy to check if a particular bug you encountered is already fixed upstream, as all bug-fixes have to land in mainline before they are considered for backporting to stable and longterm kernels.
- The situation with @kernel-vanilla/stable and @kernel-vanilla/stable-rc repositories is similar: you are just not that much ahead of Fedora’s kernels, as they often follow stable quite closely.
- The kernels from the @kernel-vanilla/fedora repository allow you to check if a bug in Fedora’s kernel is present in the stable series Fedora's kernels are based on as well. That way you can rule out if a problem might be caused by one of the patches Fedora applied.
In general, these kernels make it simple to directly interact with upstream developers. That way users don't have to bother Fedora’s kernel maintainers, which often are buried in work already -- and thus lack the manpower to look into issues that only happen in certain, not that common environments (for example only on a single Laptop).
Are the vanilla kernel packages as good as Fedora's kernel?
For many people they just as fine, but in the end they are not as good:
- The kernels shipped in the official Fedora repositories are tested by many people before they reach regular users; the kernels from the kernel vanilla repositories see no testing before being uploaded to the repositories.
- The official Fedora kernels don’t require you to turn off UEFI Secure Boot.
- The developers that take care of the kernel package in Fedora are far more experienced developers than the maintainers of the kernel vanilla repositories.
- The official Fedora kernels sometimes contain fixes for security vulnerabilities or other crucial bugs before the problem is fixed upstream; on the other hand, you often will receive fixes a bit quicker by using these repositories if they are applied upstream first.
In the end though, using kernels from the kernel vanilla repositories is not any more dangerous than installing a Linux version using the sources from kernel.org yourself.
Will everything continue to work with these kernels as it does with the official Fedora kernels?
Most of the time yes, but in a few not that common situations it might not. That’s for example the case if Fedora’s kernels include a fix for an issue not yet fixed upstream. This is not that common, but within the cards; you on the other hand sometimes get bugfixed earlier with the kernels from these repositories.
How up to date are the repositories?
Usually they are quite up to date: most of the time the repository ships snapshots daily and new releases within a few hours. But the maintainers of the kernel vanilla repositories do the work in their spare time. Occasionally a build problem or this strange thing called 'real life' come in between, which will lead to a bigger lag.
Is there any performance penalty due to debug features ?
No. The kernels shipped in these repos use a configuration nearly identical to the one used in the kernels shipped by Fedora releases, which have no debug features enabled that are known to have a significant performance overhead.
How to retrieve only mainline -rc releases from the mainline-wo-mergew copr?
The kernel vanilla repos do not support this use case, as there is no need to from the Linux perspective: -rc releases are also just snapshots, as no additional testing is performed before one is released; daily mainline snapshot thus are as reliable as -rc releases.
If you nevertheless want just -rc releases, only update the kernel only on Mondays between ~10:00 UTC and ~6:00 UTC the following day.
Are the kernels safe to use?
That depends on your definition of 'safe'.
The Linux kernel is a complex piece of software and thus contains bugs. Those bugs in the past led to data loss a few times; in extremely rare situations they even damaged hardware. Bugs like that often only show up under specific circumstances, as they otherwise likely would have been found and fixed earlier already. Specific circumstances for example can be a specific mix of hardware used in combinations with a specific kernel version built with a particular set of configuration options. Nevertheless, in the end it is unlikely that such a bug makes it into one of the non-development kernels from the kernel vanilla repositories, but there is still a very small chance for that to happen.
Note that self compiled kernels bear exactly the same risk; chances of hitting serious bugs are lower for kernels that have undergone widespread testing already, as those found in the official Fedora repositories.
In other words: The kernels from the kernel vanilla repositories will work just fine for most people. But use them at your own risk and have current backups at hand, as you always should.
Are the vanilla kernels tested before publication?
No, as they are built with Fedora’s Copr infrastructure, which doesn’t offer a simple way to test newly built packages before their publication. But all kernels shortly afterwards are booted in a virtual machine to rule out any issues; if something major is found that would affect the majority of users a package is pulled again, but that hasn't happen in a very long time for repositories containing mainline or stable kernels.
Thorsten also regularly uses the x86_64 builds from the @kernel-vanilla/mainline-wo-mergew repository, either on the latest Fedora release or a pre-release of the next one; but he doesn't reboot every day and hence won’t give each of the builds a proper field test.
Can we trust the people behind the kernel vanilla repositories?
You have to decide for yourself.
If it is any help: some people that have used or contributed to Fedora regularly will know that Thorsten (the main maintainer for these repositories) has quite a history of Fedora contributions, even if he is not very active in Fedora these days. You can assume he has no interest in ruining his reputation quickly by providing crappy packages in these repositories. On the other hand you should know that Thorsten is not a real kernel developer, so expect an occasional mistake along the way. And be reminded that using vanilla kernels has some known downsides and risks (see below).
Where to report bugs
If the Linux kernels in the packages from these repositories show any bugs please report them upstream to the Linux kernel developers, just as you would after installing a Linux kernel yourself using the sources available at kernel.org; that way all the bug reports go to the place where the people hang out that know how to fix them.
In case there are bugs in the packaging sent a mail to Thorsten Leemhuis (aka "knurd").
How can I avoid switching back and forth between vanilla kernels and Fedora kernels ?
This normally shouldn’t happen, as the kernel vanilla repositories typically contain packages package managers will consider as newer than the Fedora kernel. And if they nevertheless lag behind that’s likely because the maintainers of the kernel vanilla repositories are inactive for some good or bad reason – hence it might be wise to temporarily switch back to the Fedora kernel. If you nevertheless want to avoid that, add 'exclude=kernel*' to the first section of the following files in /etc/yum.repos.d/: fedora.repo, fedora-updates.repo, fedora-updates-testing.repo
Will this repository also ship updated userland components like drivers or udev that match the kernels in the repositories?
Normally never, as there should be no need to: the interfaces between the kernel and userland software should never change in incompatible ways; Linus Torvalds makes this pretty clear every so often.
Nevertheless in very rare situations there might be a strong reason to include such a package to avoid breakage for many users; in that case these repositories might include a package to prevent those issues.
Do you plan to provide packages for longterm (aka LTS) kernels
That’s very unlikely, as using a Linux kernel version from a series older than the one used by the particular Fedora release can lead to issues. Providing such kernels hence would not provide a good user-experience, unless Fedora itself starts to ship longterm kernels.
Additionally, the main goal of the kernel vanilla repositories for Fedora is to help upstream kernel development – longterm kernels don’t line up well with that, as they are quite a bit away from mainline development and a dead end.
Do you plan to provide packages for "linux-rt" as well?
Maybe. It depends on the interest and how hard setup and maintenance would be. Get in contact if you think investing time in these areas makes sense – or might want to help with the work.
Do you plan to provide vanilla kernels for RHEL and its derivatives?
For now it was decided to stay out of that business, even if it sounds like a good addition. There are several reasons for that. There for example are people more familiar with these distributions provide such packages already. It would mean additional work for the maintainers of this repository, too.
What configuration do those kernels use?
The configuration is pretty close to Fedora’s kernels. Which config exactly depends on the repo and branch; the kernels in @kernel-vanilla/fedora use a config that is basically identical to the kernel in the latest stable Fedora release, while those in @kernel-vanilla/mainline will be based on the config from Fedora’s rawhide kernel.
Why not put vanilla kernels in Fedora’s main repositories?
The idea is not new, but the consensus in the Fedora project as far as we can see is this: that's not a good idea, as it divides the user base; it also would make the vanilla Linux kernels more 'official' and people might simply use them without knowing their downsides. Putting the kernels in a well known and widely used external add-on repository for Fedora might make sense, but some problems would be similar.
That's the long story, rough and short. And sure, there are reasons why having vanilla kernels in the main repositories would make sense. Feel free to start a discussion on the Fedora devel and the Fedora kernel mailing list, we'll watch and might jump in.
But in the end the best approach would be to reduce the number of patches the Fedora kernel developers include to zero or something very close to that, as then some of the repos this effort provides wouldn’t be necessary at all.
Are those kernels really unpatched?
Yes, apart from a handful of very small changes that are needed for packaging.
That being said: in very rare situations we might include a patch to fix build problems. That normally only happens for mainline builds; those fixes often head upstream quickly and hence vanish from the vanilla packages pretty soon again.
Why are there no new mainline snapshots on some days?
Usually it's because nothing changed in mainline, so there was no reason to build new packages; this most commonly happens on Tuesdays and Wednesdays (UTC) during the stabilization phase.
Why so many repos? This looks stupid and over-engineered!
It can look over-engineered at the first sight, but allows us to serve multiple use-cases with nearly no overhead – and once you look closer, you'll notice that most of the time those six repositories will only contain three Linux kernel versions per Fedora Linux release.
To explain this a bit more lets take a look April 9th, 2018 while ignoring the @kernel-vanilla/stable-rc and @kernel-vanilla/next repositories to keep things simpler. Back then…
- Linux 4.17 was one week into the merge window and Linux 4.17-rc1 still one week away.
- Linux 4.16 was one week old and the first stable release 4.16.1 had just been released.
- Linux 4.15.y was still supported upstream and 4.15.16 had just been released.
At the same time…
- Fedora 29 was prepared in Rawhide, which contained a mainline snapshot (4.17-pre-rc1).
- Fedora 28 was in Beta and contained 4.16.y.
- Fedora 27 and 26 were the current releases and contained a kernel based on Linux 4.15.y.
At this particular point in time there were various users:
- Users that wanted the latest mainline snapshots (4.17-pre-rc1).
- Users that normally want the latest mainline snapshots, except during the busy merge windows when most of the changes (including all the riskier ones) happen; those users thus wanted the latest stable release instead (4.16.1).
- Users that regularly wanted to use the latest Linux stable release (4.16.1).
- Users that wanted to check if a problem they face with a Fedora kernel might be due to a patch Fedora applied to its kernels (4.16.1 for Fedora Linux 28 and 4.15.16 for Fedora Linux 27 & 26).
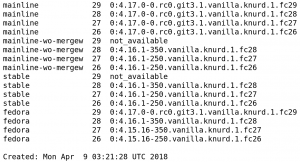
Thanks to the various coprs the kernel vanilla repositories were able to serve each of those users what they wanted:
- @kernel-vanilla/mainline shipped a mainline snapshot (4.17-pre-rc1).
- @kernel-vanilla/mainline-wo-mergew shipped the latest stable release (4.16.1).
- @kernel-vanilla/stable also provided the latest stable release (4.16.1)
- @kernel-vanilla/fedora shipped a vanilla build of the kernel version that Fedora release was using; for users of rawhide that was a mainline snapshot (4.17-pre-rc1), for users of F28 it was the latest stable release (4.16.1) and for users of F27 and F26 it was the latest stable release from the older stable series (4.15.16).
A week later when 4.17-rc1 came out the @kernel-vanilla/mainline-wo-mergew switched to shipping mainline, as the merge window was over; users of @kernel-vanilla/stable stayed on the 4.16.y series instead.
About another one-and-a-half week later Fedora made the jump to 4.16.y in F27 and F26, hence users of the @kernel-vanilla/fedora started to receive those versions, too.
FAQ for contributors and developers
Can you please include the patch found at <URL>?
No. Convince upstream to merge that patch, then the change you are interested in will automatically show up in these packages. And even better: it will automatically get into Fedora and other distributions, too!
Where is the code from which the packages are built?
You can find the code in the "ark-vanilla-*" branches of gitlab.com/knurd42/linux/; it differs only slightly from the kernel-ark infrastructure, which is used to built the SRPMs for the kernels shipped by Fedora Linux.
Note, the ark-vanilla-next and ark-vanilla-stable-rc-* branches are rebased for each build, as the Linux git tree's they are based on are regularly rebased. The ark-vanilla-mainline and ark-vanilla-stable-* branches normally are not rebased, but the former might be when kernel-ark/os-build is.
For the curious, those branches are directly or indirectly based on other branches to facilitate maintenance and avoid merge conflicts:
- The "ark-infra-*" branches (like
ark-infra-mainlineandark-infra-stable-6.2) are forks of kernel-ark branches likeos-buildandfedora-6.2containing modifications for the ark-infra needed for vanilla builds. These branches track their upstream and normally are not rebased, unless kernel-ark rebases their upstream branches (for kernel-ark/os-build this happens every nine or ten weeks right after a new mainline release). For mainline and next there are also "ark-infra-*-latest" branches, which contain additional changes from kernel-ark'skernel-ark/ark-latestbranch -- that's the one Fedora's rawhide kernels are build from that contains a few changes that have not yet reached thekernel-ark/os-build. Just like ark-latest these two branches are rebased daily.
- The "ark-patches-*" branches (like
ark-patches-mainlineorark-patches-stable-6.2) are forks of the Linux kernel upstream trees (e.g. Linus tree, linux-next, linux-6.2.y). They when needed hold patches to avoid known build-problems that would prevent vanilla builds for Fedora; such fixes are rarely needed, these branches thus most of the time do not contain any changes. They track their upstream and are rebased when they are. For stable-rc and -next this means: for every release.
- The "ark-vanilla-*" branches is where the shipped packages are build from.
All those branches are maintained by the script 'vk-gitmon.sh' which automatically or semi-automaically kicks of new builds when it notices changes in the upstream Linux branches. For mainline the process round about looks like this:
- Script notices Linux mainline was updated and merges the changes into the
mainlinebranch. - Script merges changes from
kernel-ark/os-buildintoark-infra-mainlineup to the point wherekernel-ark/ark-latestbranched off. - Script recreates
ark-infra-mainline-latestfrom currentark-infra-mainlineand merges the latest changes fromkernel-ark/ark-latest. - Script merges
mainlineintoark-patches-mainline. - Script merges
ark-patches-mainlineintoark-vanilla-mainline. - Script bulk-imports all ark infrastructure files (e.g. the redhat/ directory and a few other bits) from
ark-infra-mainline-latestintoark-vanilla-mainline. - Script tags the release and pushes the changes out.
- A gitlab webhook tells copr to start a new build.
- Copr builds the packages using the make srpm method.
This sounds overly complicated, but facilitates the maintenance and avoid merge conflicts that occured frequently with other schemes used earlier.
This structure makes it also easy to use things in other situations – for example when someone wants to create a package based on a developer tree (say "amd-staging-drm-next"): just bulk-import the a ark-infra bits from ark-infra-next-latest branch (see vkgm_update_ark_import() in vk-gitmon.sh for details) and adjust things to your needs in redhat/Makefile.variables, especially the DIST_BRANCH and UPSTREAM_BRANCH values; afterwards a command like make DISTLOCALVERSION=".amdstaging" NO_CONFIGCHECKS=1 dist-srpm allows generating a srpm.
Can I help?
Of course. Talk to Thorsten; best if you come with some ideas what you can and want to do.
Do you work together with the developers that maintain Fedora's kernel packages?
We know about each other and talk occasionally..
Please stop providing alternative kernel packages, they take attention away from the kernel packages Fedora provides and thus harm Fedora!
That's a valid concern, but we think the benefits outweigh the downsides.
That again is the long story short. Just to get a little deeper into it and show a different view on the matter at hand: similar arguments could be used to argue that Fedora should stop shipping patched kernels, as they take attention away from the upstream kernel. Up to a point such an argument is valid, too, but there are good reasons why Fedora patches its kernels.
