贡献角色
如何成为Fedora 软件包仓库维护人员?
嗯,您已经决定好了要加入了? 本指南会引领您一步一步完成您的第一个软件包维护任务。
成为Fedora 软件包仓库维护人员
请先完成以下要求
如果您还不知道如何构建一个 RPM 包,请先查阅以下帮助: How_to_create_a_GNU_Hello_RPM_package 或者更加详细的 how to create an RPM package。
阅读 Packaging Guidelines 和 Package Naming Guidelines 。
您需要十分熟悉以上内容,他们包含了许多有用的信息。当然,如果您有疑问,欢迎到 Packaging 邮件列表提问。
创建您的 Bugzilla 账户
请确保您有一个 Bugzilla 账户。
您的 Bugzilla 帐户注册时填写的邮箱应该与您在 Fedora 账户系统 中的用户所对应的邮箱地址保持一致。
订阅几个重要的邮件列表
您必须订阅 devel-announce 邮件列表。尽管这只是一个专为发布声明而设的低流量邮件列表,但是许多重要的开发信息都会在这里发布。
您也可以订阅 devel 邮件列表,这是个有关 Fedora 开发的讨论邮件列表,不过请注意流量比较大。
您也可以考虑订阅 package-announce 邮件列表。当软件仓库的软件有变动的时候,邮件列表会有提示。本列表流量十分高,因为每次软件包的改动都会触发系统发送邮件。
当然,查看以前的存档,请订阅 packaging 邮件列表,这是 Fedora 打包委员会 的专用邮件列表。委员们决定有关 Fedora 的软件规定。
确保您的软件包适合 Fedora 项目
你提交的软件包可是任何种类的开源自由软件,当然最重要的是在我们的源里面尚未被收录。在创建您的软件包之前,请确保该软件包不在仓库中而且尚未处于被审核状态(之前有人已经制作好了,正在提请官方审核)。
因此请一定完成以下4步,然后再考虑提交:
- 搜索 Fedora 软件包数据库以便了解您要提交的软件包是否已经存在。
- 搜索 Review Tracker(审核跟踪器)以便了解哪些软件包正处于被审核状态。
- 检查 已废弃的软件包 列表。
- 注意 禁止提交的软件包。
理解您的责任
Fedora 项目收录的软件包需要被经常维护。尤其是软件有安全更新时,更需要您不断地维护。作为一名 Fedora 项目的软件包维护人员,您需要明确自己的 职责 。我们鼓励您成为一个或多个软件包的 副维护人员 ,当您需要帮助时,请在 Fedora 社区的有关开发的邮件列表中寻找答案。
参阅其他意见
Read some other package submissions to learn about packaging and gain familiarity with the process and requirements.
One way of doing this is to join the package-review@lists.fedoraproject.org mailing list ; all comments on Fedora package reviews are sent to this (read-only from your point of view) list.
制作一个软件包
- 如果您不知道如何构建 RPM 包,请移步这里:如何制作 RPM 包 。
- 确保您的软件包符合 打包规定 和 软件包命名规定 。
- 留意 软件包审核规定 (日后审核时需要)。
上传您制作的软件包
上传您制作的源代码 RPM 包和与之相匹配的 SPEC 配置文件到互联网的任意位置上。请确保其可以通过地址访问。如果您已经有了一个 Fedora 帐户,您也可以使用位于 http://fedorapeople.org 的空间来存放。
申请审核您提交的软件包
请先填表: https://bugzilla.redhat.com/bugzilla/enter_bug.cgi?product=Fedora&format=fedora-review
- 在您提请审核前,确保之前没有人在做与您相同的事。
- Make sure that you put the name of the package (excluding version and release numbers) in the '
Review Summary' field, along with a very brief summary of what the package is. - Upload the spec file and SRPM to a public website. If you need hosting space, please make a note of it in your ticket submission and someone will take care of you. If you are a Fedora package maintainer already, you can make use of http://fedorapeople.org
- Put a description of your package (usually, this can be the same thing as what you put in the spec %description) in the '
Review Description' field. Include the URLs to your SRPM and SPEC files. Also, explain that this is your first package and you need a sponsor.
具体我们是如何审核您制作的软件包的,请访问 Package Review Process 页面。
通知上游相关人员
Fedora as a project prefers to stay close to upstream. Inform the developers that you are packaging the software. You can do that by sending them an email introducing yourself and pointing out the review request. This sets up the stage for future conversations. They will usually advertise the fact that their software is now part of Fedora or might want to inform you of important bugs in the existing release, future roadmaps etc.
介绍自己
当一个新的软件包维护人员加入 Feodra 项目时,我们需要您在 devel 邮件列表介绍一下您自己。请访问 devel ,然后加入订阅。我们需要您这么做主要目的是建立大家之间的信任,当然也有助于大家了解您和软件包被审核成功的几率。
我们这么做还为了打破匿名氛围,并且培养一个项目内的真实世界。您不必透露自己的一些秘密,我们的目标只是建立成员间的友谊。
自我介绍信格式:
邮件主题: Self Introduction: 您的姓名
正文: 您想些什么都可以,建议附上您的 GPG 密钥代码。
留意用户反馈
初次加入请注意 Bugzilla 的报告。一旦用户有反馈,您会收到相关邮件。 尽可能修复用户提出的 Bug 。
创建一个 Fedora 帐户
首先在 Fedora 账户系统 新建您的个人账户。注意,它不仅用于 Bugzilla !
- 1、访问: https://admin.fedoraproject.org/accounts/
- 2、点击 'New account' 然后填写必填信息
- 3、After you create your account, please be sure to sign the CLA (if you click on the "My Account" link in the top right, you should see CLA: CLA Done).
- Also you need to upload a public RSA SSH key. You need to use the matching private key to access Fedora machines via SSH
安配置本地环境(Koji)
To build Packages for the Fedora Collection or EPEL, you need Koji.
You'll also need to generate a client side certificate at the Fedora Account System and save the file in ~/.fedora.cert, where fedpkg will look for it by default.
The fedora-packager package provides tools to help you setup and work with fedora, therefore install it:
yum install fedora-packager
After installation run it as your user to setup your koji configuration:
fedora-packager-setup
You can now use "koji" to try to build your RPM packages on platforms (e.g., PPC) or distributions you don't have. Note that you can test out builds ("scratch" builds) even when your package hasn't been approved and you don't have a sponsor. A simple way to do a scratch build using koji is to do this at the command line:
koji build --arch-override=PLATFORM --scratch TARGET path_to_source_RPM
Where:
- PLATFORM is a platform keyword such as i386 (32-bit), x86_64, ppc, or ppc64. You can omit --arch-override=PLATFORM, in which case koji will do test builds on all the architectures the spec file says the package supports.
- TARGET is a distribution keyword such as dist-f9 (for Fedora 9). You can run "koji list-targets" to see all targets. To build for the next release (rawhide), don't use "dist-rawhide" - use "dist-fX" where X is one more than the latest stable release.
- Note that you need to supply the path to the source RPM (which ends in .src.rpm), and not a URL. (If you only have the spec file, use
rpmbuild --nodeps -bs SPECFILEto create the new source RPM).
Your koji builds can only depend on packages that are actually in the TARGET distribution repository. Thus, you can't use koji to build for released distributions if your package depends on other new packages that Bodhi hasn't released yet. You can use koji to build for rawhide (the next unreleased version), even if it depends on other new packages, as long as the other packages were built for the "rawhide" as described below. If you need to build against a package that is not yet a stable released update, you can file a ticket with rel-eng at: https://fedorahosted.org/rel-eng/newticket and request that that package be added as a buildroot override. For packages in EPEL, you have to use the component epel to get the request to the right persons.
You can learn more about koji via:
koji --help # General help koji --help-commands # list of koji commands koji COMMAND --help # help on command COMMAND
Using_the_Koji_build_system has more information about using Koji.
得到认可
When the package is APPROVED by the reviewer, you must separately obtain member sponsorship in order to check in and build your package. Sponsorship is not automatic and may require that you further participate in other ways in order to demonstrate your understanding of the packaging guidelines. Key to becoming sponsored is to convince an existing sponsor-level member that you understand and follow the project's guidelines and processes.
See how to get sponsored into the packager group for more information on the process of becoming sponsored.
Your sponsor can add you to the packager group. You should receive email confirmation of your sponsorship.
Add Package to Source Code Management (SCM) system and Set Owner
If you are becoming a maintainer for a new package, instead of being a co-maintainer, follow Package SCM admin requests to get a module for your new package and branches for recent releases.
This will be used to set up the proper records in the owners database, which is used for access to build the package, bugzilla population, and other features. This step creates a module in the repository your new package, with branches for each requested distribution.
Check out the module
You could check out your module now, but before doing that, consider doing "mkdir ~/fedora-scm ; cd ~/fedora-scm" - that way, all your files are inside that. Also, run ssh-add, so that you won't have to keep typing in your key password.
Now you are ready to checkout your module from the SCM:
fedpkg clone <packagename>
Where <packagename> should be replaced with the name of your package.
测试您制作的软件包
Refer to Using_Mock_to_test_package_builds and Using_the_Koji_build_system#Scratch_Builds for more information on testing your package. Mock uses your local system while Koji command line tool uses the Fedora build system server.
Import, Commit,and Build Your Package
Now that you've checked out your (empty) package module with fedpkg, cd into the module's master branch:
cd <packagename>
Run fedpkg to import the contents of the SRPM into the SCM:
fedpkg import PATH_TO_SRPM
# Review Changes, press 'q' to stop; Revert with: git reset --hard HEAD git commit -m "Initial import (#XXXXXX)." git push fedpkg build
Obviously, replace PATH_TO_SRPM with the full path (not URL) to your approved SRPM, and XXXXXX with the package review bug number.
This imports into, commits, and builds only the master (rawhide) branch.
If the commit fails with this kind of message:
W access for why DENIED to YOUR_ACCOUNT fatal: The remote end hung up unexpectedly Could not push: Command '['git', 'push']' returned non-zero exit status 128
Then you don't have the necessary rights to modify that package branch; view https://admin.fedoraproject.org/pkgdb/acls/name/PACKAGE_NAME to request those rights.
更新软件包分支(如果需要)
Branches are f# (formerly F-# and before that FC-#), master, etc. So f16 is the branch for Fedora 16.
To switch to a branch first:
fedpkg switch-branch BRANCH (e.g. f16)
Merge the initial commit from master, creating an identical commit in the branch:
git merge master
Push the changes to the server:
git push
Build the package:
fedpkg build
If there is another branch to work with repeat "To switch to a branch" and import and commit to each branch
If everything goes well, it should queue up your branch for building, the package will cleanly build, and you're done!
If it fails to build, the build system will send you an email to report the failure and show you to the logs. Commit any needed changes to git, bump the SPEC release number, and request a new build.
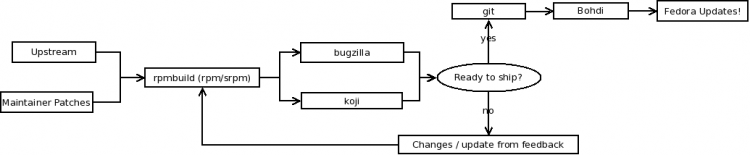
在Bodhi系统中提交软件包更新
The Fedora update system called Bodhi is used for pushing updates, classifying packages etc. Do not submit "master" (aka rawhide) packages via bodhi.
You can push an update using Bodhi via the command line using this in each branch:
fedpkg update
You can also use "bodhi" command directly as described in the Bodhi Guide.
You can also use the Web interface for Bodhi to request enhancement updates for each released Fedora you are bringing a new package to.
The first field asks for the name of the "Package". This field will auto-complete the package name found in the Koji build system, e.g. <package-name>-<version>-<release>.fc16. If completion doesn't work, just enter the package build name yourself.
For new packages, choose "newpackage" as the "type" of update.
Put the "Request" as "testing" if you want to put the package through testing first, see Fedora Quality Assurance . Put "stable" if you want to push the package directly to stable.
Put the bug number of the package's Review Request in the "Bugs" field blank. Bodhi will automatically close it as NEXTRELEASE when it gets pushed to the requested update status.
For new packages, add a copy of the package's description in the "Notes" section, so end users will know what the package is.
Here is the Bodhi Guide and more information on Bodhi .
After you have submitted an upgrade through bodhi, your package is placed in a queue. Periodically, an administrator will check the queue and push all of the packages into the appropriate repositories.
Make the package available in "comps" files
If appropriate for the package, make it available in "comps" files so that it can be selected during installation and included in yum's package group operations. See PackageMaintainers/CompsXml for more info.
等待源最后更新
Fedora has infrastructure available for monitoring new upstream releases of the software you are packaging. Refer to Upstream Release Monitoring for more details. Learn to handle updates by reading the Package update HOWTO
得到帮助
我们也知道这项工作有时候真的很烂,但是我们一直尝试把它做得更好。如果您陷入问题的怪圈中,请在 devel@lists.fedoraproject.org 邮件列表或者位于 freenode.net 的 IRC 频道 #fedora-devel[?] 提问。
The Fedora Mentors Project has people willing to help new contributors in their packaging efforts. See the Mentors page for more information.
您也可以查阅 using git FAQ for package maintainers 。
维护一个在仓库中已存在的软件包
如果您已经参与维护仓库中的一个软件包,并且有意愿维护另一个时,请查阅这个:指南 以完成您的心愿。