貢献という役割
Fedora パッケージコレクションメンテナへの参加方法
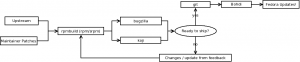
本当にあなたは Fedora プロジェクトのパッケージメンテナになることを決意しましたか?これはあなたが最初のパッケージを投稿するまでのガイドです。
Fedora パッケージコレクションメンテナになる
ガイドラインを読む
もしあなたが RPM パッケージの作成方法を知らないなら、簡易 RPM チュートリアルか、より高度で詳細な内容の RPM パッケージの作成方法を参照してください。
そしてパッケージングガイドライン と パッケージ名ガイドラインを読んでください。
あなたは RPM パッケージングに十分に精通する必要があります。RPM パッケージングの知識は全てのパッケージ投稿に影響を与えます。もし質問があれば、Fedora パッケージングメーリングリストで尋ねてください。
Bugzilla アカウントを作成する
Red Hat Bugzilla にアカウントを作成してください。
Bugzilla のアカウントで使用するメールアドレスは、Fedora パッケージングの全ての関連事項を扱うために Fedora アカウントシステムで使用するメールアドレスと同じメールアドレスを使用すべきです。
重要なメーリングリストへ参加する
あなたは fedora devel-announce@lists.fedoraproject.org メーリングリストへ参加しなければなりません。それは流通量の少ないアナウンス用のメーリングリストで、重要な開発情報が投稿されます。
fedora devel@lists.fedoraproject.org メーリングリストに参加することもできます。そこでは開かれた Fedora 開発に関して議論されます。これは流通量の多いメーリングリストです。
さらに package-announce@lists.fedoraproject.org に参加することも考慮してください。Fedora リポジトリの全パッケージのコミット通知を取得するためのコミット情報のメーリングリストです。これはかなり流通量が多いメーリングリストです。Fedora パッケージデータベースは、あなたが(共同で)メンテナンスするパッケージのためにコミットメールを送信します。
参加した方が良いと見なされる(少なくともアーカイブを見れる方が良い)他のメーリングリストは packaging@lists.fedoraproject.org です。これは Fedora プロジェクトの公式パッケージングガイドラインを決定する Fedora パッケージング委員会のメーリングリストです。
パッケージが適切なものだと保証する
あなたが投稿するパッケージは既に Fedora でパッケージングされていない、フリーでオープンソースなプロジェクトになります。あなたのパッケージを作成する前に、そのソフトウェアが Fedora リポジトリに既に存在していないか、又はレビュー待ち状態でないかを確認してください。
- 既にリポジトリにパッケージが存在していないかを Fedora パッケージデータベースで検索してください。
- レビュー待ち状態でないかを レビュートラッカ で検索してください。
- さらに 関連パッケージリストを確認してください。
- 隠されたアイテムに注意してください。
他の提案を読む
パッケージングに関して学ぶために他の人のパッケージ投稿を読んで、そのプロセスや要求に精通してください。
そうするための1つの方法は package-review@lists.fedoraproject.org メーリングリストに参加することです。Fedora パッケージレビューの全てのコメントがこのメーリングリスト(あなたの視点からだと読み専用)に送られます。
パッケージを作る
- もし RPM パッケージを作成する方法を知らないなら RPM パッケージの作成方法を参照してください。
- あなたのパッケージが パッケージングガイドラインと パッケージング名ガイドラインに準拠しているかを確認してください。
- パッケージレビューガイドラインに注意してください(パッケージレビューに使用されます)。
パッケージをアップロードする
SRPM と spec ファイルをインターネット上のどこかにアップロードしてください。それは URL でどこからでもアクセスできる場所になります。 あなたが既に Fedora アカウントを持っているなら、そのためのストレージとして http://fedorapeople.org を使用することができます。
レビューリクエストを作成する
https://bugzilla.redhat.com/bugzilla/enter_bug.cgi?product=Fedora&format=extras-review のフォームに記入してください。
- あなたのリクエストを投稿する前に同じパッケージに対して直前のリクエストがないかを確認してください。
- そのパッケージが何なのかを説明する 短い要約 を添えて '
Review Summary' フィールドに パッケージ名 (バージョンとリリース番号を除く) があることを確認してください。
- spec ファイルと SRPM を公開されたウェブサイトへアップロードしてください。もしホスティングスペースが必要なら、チケット投稿の際にメモとして書いておくと誰かが面倒を見てくれるでしょう。あなたが既に Fedora パッケージメンテナなら http://fedorapeople.org を使用して作ることができます。
- あなたのパッケージの 説明 (通常は spec ファイルの %description に追加する内容と同じ説明)を '
Review Description' フィールドに追加してください。そして、あなたの SRPM や SPEC ファイルへの URLs を含めてください。さらにこれはあなたの最初のパッケージでスポンサーが必要であることも説明してください。
レビュープロセスの詳細は パッケージレビュープロセスページを参照してください。
アップストリームへ知らせる
プロジェクトとしての Fedora は アップストリームに近い状態を維持することを好みます。あなたがパッケージングしていることをそのソフトウェアの開発者へ知らせてください。自己紹介のメールを送ったり、レビューリクエストで指摘したりすることで自分がパッケージングを行っていると知らせることができます。これは今後の会話の場を提示します。彼らのソフトウェアが現在は Fedora の一部であるという事実を通常は公示するか、既存リリースの重要なバグ、今後のロードマップ等があればあなたに知らせたくなるかもしれません。
フィードバックを監視する
あなたの最初のパッケージの Bugzilla レポートを監視してください。メールで変更通知を受け取るべきです。レビューアが blocker だと指摘したらとにかく修正してください。
Fedora アカウントを取得する
Create an account in the Fedora Account System (this is not just a bugzilla account)
- Visit the account system home: https://admin.fedoraproject.org/accounts/
- Click on 'New account' and fill in the blanks.
- After you create your account, please be sure to sign the CLA (if you click on the "My Account" link in the top right, you should see CLA: CLA Done)
Note: Red Hat employees should apply forcla_redhatinstead. From the Account System, Apply for a New Group, putcla_redhatin the group field, and click Apply. Then ask TomCallaway to approve you.
クライアントツール(Koji)をインストールする
To build Packages for the Fedora Collection or EPEL, you need Koji.
You'll also need to generate a client side certificate at the Fedora Account System and save the file in ~/.fedora.cert, where fedpkg will look for it by default.
The fedora-packager package provides tools to help you setup and work with fedora, therefore install it:
yum install fedora-packager
After installation run it as your user to setup your koji configuration:
fedora-packager-setup
You can now use "koji" to try to build your RPM packages on platforms (e.g., PPC) or distributions you don't have. Note that you can test out builds ("scratch" builds) even when your package hasn't been approved and you don't have a sponsor. A simple way to do a scratch build using koji is to do this at the command line:
koji build --arch-override=PLATFORM --scratch TARGET path_to_source_RPM
Where:
- TARGET is a distribution keyword such as dist-f9 (for Fedora 9). You can run "koji list-targets" to see all targets. To build for the next release (rawhide), don't use "dist-rawhide" - use "dist-fX" where X is one more than the latest stable release.
- PLATFORM is a platform keyword such as i386 (32-bit), x86_64, ppc, or ppc64. You can omit --arch-override=PLATFORM, in which case koji will do test builds on all the architectures the spec file says the package supports.
- Note that you need to supply the path to the source RPM (which ends in .src.rpm), and not a URL. (If you only have the spec file, use
rpmbuild --nodeps -bs SPECFILEto create the new source RPM).
Your koji builds can only depend on packages that are actually in the TARGET distribution repository. Thus, you can't use koji to build for released distributions if your package depends on other new packages that Bodhi hasn't released yet. You can use koji to build for rawhide (the next unreleased version), even if it depends on other new packages, as long as the other packages were built for the "rawhide" as described below. If you need to build against a package that is not yet a stable released update, you can file a ticket with rel-eng at: https://fedorahosted.org/rel-eng/newticket and request that that package be added as a buildroot override. For packages in EPEL, you have to use the component epel to get the request to the right persons.
You can learn more about koji via:
koji --help # General help koji --help-commands # list of koji commands koji COMMAND --help # help on command COMMAND
Using_the_Koji_build_system has more information about using Koji.
スポンサーを得る
When the package is APPROVED by the reviewer, you must separately obtain member sponsorship in order to check in and build your package. Sponsorship is not automatic and may require that you further participate in other ways in order to demonstrate your understanding of the packaging guidelines. Key to becoming sponsored is to convince an existing sponsor-level member that you understand and follow the project's guidelines and processes.
See how to get sponsored into the packager group for more information on the process of becoming sponsored.
Your sponsor can add you to the packager group. You should receive email confirmation of your sponsorship.
ソースコード管理(SCM)システムへパッケージを追加して所有者をセットする
Follow Package SCM admin requests to get a module for your new package and branches for recent releases.
This will be used to set up the proper records in the owners database, which is used for access to build the package, bugzilla population, and other features. This step creates a module in the repository your new package, with branches for each requested distribution.
そのモジュールをチェックアウトする
You could check out your module now, but before doing that, consider doing "mkdir ~/fedora-scm ; cd ~/fedora-scm" - that way, all your files are inside that. Also, run ssh-add, so that you won't have to keep typing in your key password.
Now you are ready to checkout your module from the SCM:
fedpkg clone -B <packagename>
Where <packagename> should be replaced with the name of your package.
You should now have a directory named after your package with a directory for each branch inside of it.
パッケージをインポートする
Now that you've checked out your (empty) package module with fedkpkg, cd into the module:
cd MODULE_NAME
Run the fedpkg, to import the contents of the SRPM into the SCM:
fedpkg import PATH_TO_SRPM (Review Changes) fedpkg commit -p
Obviously, replace PATH_TO_SRPM with the full path (not URL) to your approved SRPM.
This imports into only the master (rawhide) branch.
You will probably also want to do additional imports using the -b parameter, which will import the package into other distribution branches like F-9, e.g.:
./common/cvs-import.sh -b F-9 PATH_TO_SRPM
The cvs-import.sh program will respond with:
Checking out module: 'NAME'
You may see errors like this several times, these can be ignored:
buffer_get_ret: trying to get more bytes 129 than in buffer 34 buffer_get_string_ret: buffer_get failed buffer_get_bignum2_ret: invalid bignum key_from_blob: can't read rsa key key_read: key_from_blob AA.... failed
But among them you should see:
Unpacking source package: NAME....src.rpm...
Along with a list of the source files in the source package, followed by checking and uploading of the files.
)
Then, you'll see "If you want to make any changes before committing, please press Ctrl-C. Otherwise press Enter to proceed to commit." Press Enter.
Finally (if you haven't set up an other editor) vi will open up to let you edit the changelog. For the changelog, use the same format as the end of the .spec file. If you haven't used vi yet, after entering your changelog press 'Enter' and type
:wq
and press 'Enter' again to finish the import.
ブランチを更新する
Branches are f# (formerly F-# and before that FC-#), master, etc. So f13 is the branch for Fedora 13.
However, your local directory may not have exactly the right versions of the files, so go into the branch directory (e.g. cd devel/ or cd f12/) and run:
git pull
ビルドをリクエストする
For each branch that you'd like to request a build for, go into the branch directory (e.g. cd f13/) and run:
fedpkg build
If everything goes well, it should queue up your branch for building, the package will cleanly build, and you're done!
If it fails to build, the build system will send you an email to report the failure and show you to the logs. Commit any needed changes to cvs, bump the SPEC release number, and request a new build.
Bodhi へ至るものとしてパッケージを投稿する
The Fedora update system called Bodhi is used for pushing updates, classifying packages etc. Do not submit "master" (aka rawhide) packages via bodhi.
You can push an update using Bodhi via the command line using:
fedpkg update
You can also use "bodhi" command directly as described in the Bodhi Guide.
You can also use the Web interface for Bodhi to request enhancement updates for each released Fedora you are bringing a new package to.
The first field asks for the name of the "Package". This field will auto-complete the package name found in the Koji build system, e.g. <package-name>-<version>-<release>.fc9. If completion doesn't work, just enter the package build name yourself.
For new packages, choose "newpackage" as the "type" of update.
Put the "Request" as "testing" if you want to put the package through testing first, see Fedora Quality Assurance . Put "stable" if you want to push the package directly to stable.
Put the bug number of the package's Review Request in the "Bugs" field blank. Bodhi will automatically close it as NEXTRELEASE when it gets pushed to the requested update status.
For new packages, add a copy of the package's description in the "Notes" section, so end users will know what the package is.
Here is the Bodhi Guide and more information on Bodhi .
After you have submitted an upgrade through bodhi, your package is placed in a queue. Periodically, an administrator will check the queue and push all of the packages into the appropriate repositories.
パッケージを "comps" ファイルで利用可能状態にする
If appropriate for the package, make it available in "comps" files so that it can be selected during installation and included in yum's package group operations. See PackageMaintainers/CompsXml for more info.
アップデートを監視する
Fedora has infrastructure available for monitoring new upstream releases of the software you are packaging. Refer to Upstream Release Monitoring for more details. Learn to handle updates by reading the Package update HOWTO
ヘルプを取得する
We know that this process can be as clear as mud sometimes, and we're always trying to make it better. If you run into any problems, or have any questions, please ask on the devel@lists.fedoraproject.org mailing list or in #fedora-devel on freenode . See the Communicate page for details.
The Fedora Mentors Project has people willing to help new contributors in their packaging efforts. See the Mentors page for more information.
See also using git FAQ for package maintainers.
既存のメンテナのために Fedora パッケージコレクションに新たなパッケージを入れる
あなたが既に Fedora のパッケージをメンテナンスしていて他のパッケージをメンテナンスしたいなら、既存の貢献者のための新たなパッケージプロセスに従うようにしてください。

