How comps is used
Installation
comps is used by the installer during software selection. At the installer software selection dialog, the user can choose between a variety of Environments on the left, and Options to those environments on the right.
Each environment consists of a list of groups, and a list of groups that are options for that environment. The list of available options is supplemented by any groups that are marked as 'uservisible' in the comps file.
Installation (releases prior to Fedora 18)
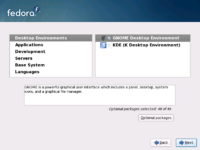
comps is used by the installer during package selection. At the Default Packages dialog , the user can choose to Customize Now, displaying the Category Selection dialog.
In the category selection dialog , categories (as defined by the category keyword in <file>comps.xml</file>) are listed down the left-hand side. If a category is selected, any groups in that category with uservisible set are displayed in the right-hand pane. Groups have an icon associated with them. These icons come from the comps-extras package; icons are read from /usr/share/pixmaps/comps/<group-id>.png. If an icon does not exist for a group id, the one for the category that the group is in is used.
Once a group is selected, clicking the Optional Packages button shows
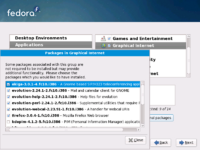
Package Selection dialog.
In any group, there are four levels of packages: optional, default, mandatory, and conditional:
optionalare not automatic but can be checkeddefaultare, but can be unchecked in a gui toolmandatoryare always brought in (if group is selected), and not visible in the Package Selection dialog.conditionalare brought in if theirrequirespackage is installed
Usually optional is the way, however if you feel that your package deserves a default or required level bring it up for discussion on the development lists. Remember that this has effect on whether or not your package winds up on distribution media such as Live images and spins.
Running System
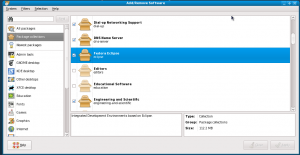
In yum, groups are used by yum groupinstall and yum groupremove commands, and can be queried with yum grouplist command.
In PackageKit (Add / Remove Software) the upper left quadrant shows Package collections. When this is clicked, the grouping information is loaded from the configured software repositories, and the complete list of groups, stripped from their categories, are shown in the right hand pane. Selecting a group for installation causes only the default packages within the group to be installed.
Tree, Release, and Image Composition
The kickstart files in spin-kickstarts use the group definitions from comps to compose images and release trees.
When to Edit comps
- If your app should be part of one of the installation environments, or part of an option for one of them, it should be included
- If you're creating a new option for an installation environment
- Libraries should not be included - they will be pulled in via dependencies
- Most text-mode utilities don't really fit in unless they have a pretty large established user-base.
If you have questions as to whether it makes sense or not, feel free to post to the development list.
Some guidelines on specific groups in comps follows.
New groups
Please consult devel@lists.fedoraproject.org before adding new groups.
New user-visible group names and descriptions are translatable strings. Do not add new groups, or change their descriptions, during a string freeze. Please check the release schedule for these dates.
Core
Core is not visible, so adding 'default' or 'optional' packages to it isn't needed. Boot loaders are listed as 'default' in the group so that they're pulled in by compose tools.
Core is installed on every installation, so adding packages to it is discouraged.
GNOME Desktop
The gnome-desktop group and GNOME environment definition is maintained by the Desktop SIG. Please run changes through desktop@lists.fedorarproject.org.
KDE Desktop
The kde-desktop group and KDE environment definition is maintained by the KDE SIG. Please run changes by them.
Fonts
The following is part of the Fonts SIG packaging rules.
Fonts for a particular linguistic region used to be bundled in fonts-region packages. Nowadays this practice is frowned upon, fonts package naming reflects upstream naming like in any other Fedora package, and grouping is achieved through comps groups.
- Font packages in a legacy format (not TTF or OTF) MUST be registered in the legacy-fonts group.
- Font packages in a non-legacy format (TTF or OTF):
- MUST be registered in the fonts group:
- except when they don't have an active upstream, in which case putting them in legacy-fonts is fine.
- SHOULD also be registered in every applicable xxx-support localization group:
- except groups that only require glyphs in the basic latin range.
- if a font package adds support for a script previously not supported by Fedora the associated localization groups MUST be created and filed, and the relevant localization teams notified.
- SHOULD be declared optional, unless:
- they add support for a new script, in which case they MUST be declared required in the associated localization groups.
- they add better support for already supported scripts, in which case, if the localization team in charge of each localization group agrees:
- they can replace existing fonts as mandatory if this script is not covered by distribution-wide default fonts.
- they can replace existing fonts as default if this script is covered by distribution-wide default fonts.
- MUST be registered in the fonts group:
Language support groups
Language support groups are selected automatically if you are installing in the specified language, and manually otherwise. Language support groups require the langonly key, which should be set to ISO 639-1 two-letter language code for that language, or the ISO 639-2 bibliography code, if that does not exist.
These codes can be looked up in the iso-codes package.
Each language support group should have mandatory packages for:
- fonts required for that locale (consult the Fonts SIG)
- input methods, and data, required for that locale (consult the I18N SIG)
Each language support group can have optional packages for:
- additional fonts that support that locale (consult the Fonts SIG)
New language support groups need added to the language-support category in the comps file.
All other groups
When making changes to the default or mandatory packages, strive for consensus, and consult the development lists as necessary. If you're unsure, you can also file a bug against the comps component in bugzilla.
How to edit comps
Clone the comps GIT module in Fedora Hosted:
git clone ssh://username@git.fedorahosted.org/git/comps.git
Find a reasonable group in the comps-fnxml.in file (where n represents the release number) for your package. If your package is not listed there, please add it using the following as a template if your package were named "foo":
<packagereq type="optional">foo</packagereq>
- Make sure to preserve the alphabetical order in each group.
- Make sure to run xmllint on the result to check you didn't make a mistake in the XML syntax.
You can use the provided xslt filter to sort, indent and check the syntax of your comps file in one run:
$ xsltproc --novalid -o sorted-file comps-cleanup.xsl original-file
The filter will warn you if it removes redundant information or if something needs to be checked by a human.
Commit your changes (git commit -a). You
can then push your changes to the repository with git push.
Please make sure to run git pull --rebase right before git push to
avoid overwriting other people's changes as much as possible.
Current status
You can check our current comps status file here.
