Firefox Hardware acceleration on Fedora
Firefox on Fedora supports hardware acceleration on Linux so let's look how to configure it and diagnose potential issues. This guide is adjusted for Fedora only and may not work for stock Mozilla binaries or other distros.
Web page rendering
Accelerated web page rendering is supported on both X11 and Wayland backends via WebRender.
Please note that Firefox requires a GPU with support for OpenGL 3.2 or newer or GLES 3.0 or newer to enable hardware acceleration (Source and further info). You can check your hardware using glxinfo | grep "profile version" for OpenGL and eglinfo | grep version for GLES.
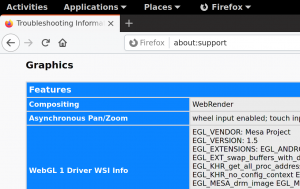
You can check hardware acceleration state at about:support page, look at Compositing row. If there's WebRender, you're running on hardware. If there's WebRender (software) you're on non-accelerated backend.
Web page rendering on Wayland
Hardware acceleration should work out-of-the-box on Wayland. If not please file a bug for it.
Web page rendering on X11
X11 backend can tun in two modes - EGL and XGL. You should be on EGL unless you're running NVIDIA proprietary drivers.
Video decoding
Hardware accelerated video decoding (for video playback or for WebRTC) is available on Intel/AMD via VA-API for both X11(EGL) and Wayland and can be enabled by preferences at about:config.
Right now it's blocked by RDD Firefox sandbox. RDD is a new sandboxed process used for safe video decoding. You can disable it which reverts Firefox back to state before RDD implementation which means video decoding will run under content sandbox which is less restrictive.
Video decoding on AMD
Accelerated video decoding works well on AMD as free drivers are available. You can enable it by these steps:
- Verify you're running on HW accelerated backend (WebRender) under Wayland or X11/EGL at about:support.
- Install ffmpeg, libva and libva-utils from RPM Fusion repository.
- Run vainfo on terminal to verify that VA-API works.
- At about:config page set media.ffmpeg.vaapi.enabled to true and media.rdd-process.enabled to false. Warning: Disabling the RDD process sandbox is a security risk!
- Restart browser.
- You may install enhanced-h264ify Firefox extension to disable non-accelerated video formats.
- More info is here.
Video decoding on Intel
Accelerated video decoding works well on most Intel GPUs as free drivers are available. There are two[1] drivers for Intel cards, libva-intel-driver (provides i965_drv_video.so) and intel-media-driver (iHD_drv_video.so). Currently, Firefox works with libva-intel-driver (i965_drv_video.so) only, intel-media-driver is broken due to Firefox sandboxing issues. I strongly recommend to avoid it at all cost and don’t disable content sandbox for it, your web browser will be completely naked then.
You can enable VA-API on Intel by these steps:
- Verify you're running on HW accelerated backend (WebRender) under Wayland or X11/EGL at about:support.
- Install libva, libva-utils, and libva-intel-driver packages.
- Install ffmpeg from RPM Fusion repository.
- Run vainfo on terminal to verify that VA-API works. If VA-API is disabled you're running on new hardware[2] and you need intel-media-driver from RPM Fusion repository non-free. Don't use that until content sandbox is fixed.
- At about:config page set media.ffmpeg.vaapi.enabled to true and media.rdd-process.enabled to false. Warning: Disabling the RDD process sandbox is a security risk!
- Restart browser.
- You may install enhanced-h264ify Firefox extension to disable non-accelerated video formats.
- More info is here.
Video decoding on NVIDIA
Please buy some real Linux hardware.
Troubleshooting
Run Firefox on terminal with MOZ_LOG="PlatformDecoderModule:5" env variable. It produces a playback and decode log with VA-API / ffmpeg details.
Video encoding
Hardware accelerated video encoding (for WebRTC for instance) is not supported/implemented in Firefox, no matter which preference you set at about:config page.
