NOTE: Portions of this document are being reworked to integrate the QMF framework
Authors
John (J5) Palmieri
Abstract
This proposal outlines the publish/subscribe infrastructure for notification within the Fedora Infrastructure pieces using the AMQP protocol, MRG Messaging services and the QMF object framework. Where possible library interaction will be described as a generic publish/subscribe layer over the complexities of AMQP/QMF. While the QMF protocol gives suggestions on naming conventions, this document will attempt to solidify best practices when dealing with namespaces inside the Fedora Infrastructure universe.
Definitions
- address - internet URI for connecting to broker
- broker - a simplification of the AMQP exchange/binding/queue concept. A broker routes and relays messages to their intended recipients. Intermediate brokers can be used to relay messages to specific security domains. For instance bodhi and koji wouldn't send messages directly to subscribers, they would send messages to only routers they trust such as the fedora community broker. In turn applications running in fedora community would trust the FComm router is sending them messages from koji and bodhi and not some other source. A similar broker can be run for desktop apps which would require individual FAS tokens to be able to monitor resource usage.
- callback - a function that is called in response to an incoming message
- client - any application publishing or consuming messages through AMQP
- event - identifier for the message being sent, e.g. koji would send build_started, build_finished events
- package - identifier for specific publishers, e.g. koji would identify itself as the org.fedoraproject.koji package
- payload - data QMF format sent with the signal
- publisher - any client sending messages in AMQP
- subscriber - any client consuming messages in AMQP
Physical Layout
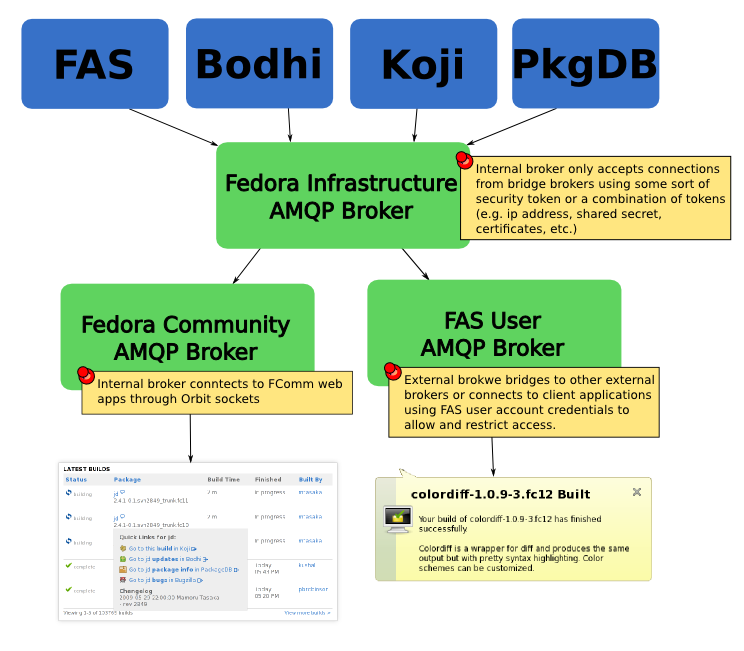
Because we need to be able to control access in order to not overload our servers/bandwidth and to provide security the AMQP routers need to be split into different security domains, each with their own access rules and purpose.
Fedora Infrastructure AMQP Broker
This is the service that all Fedora Infrastructure applications publish notifications through. It is internal and only allows internal services publish and subscribe on it. It can do this through several methods including, an ip/domain white list, shared secrets (aka passwords), certificates and physical isolation from external networks. Everything published on this broker will be trusted by the downstream brokers as being correct. Downstream brokers will not be able to publish, only subscribe to messages on this broker.
Fedora Community AMQP Broker
This broker listens to messages from the Fedora Infrastructure Broker (as well as any other notification sources such as upstream). It then sends this message over an Orbit socket to any Fedora Community web app subscribed. Browser domain security ensures that only apps coming from the Fedora Community server can create a connection. This Broker is internal and relies on an Orbit bridge to communicate with external browsers. Applications are not yet allowed to publish messages to Fedora Community (they have to use the normal REST interfaces) though it might be interesting to see if we can export the REST interfaces over this bridge.
FAS User AMQP Broker
This broker listens to messages from the Fedora Infrastructure Broker (as well as any other notification sources such as upstream) and allows external applications to become AMQP clients. This is an external broker and is locked down via FAS user and group authentication. This allows fine grained control over access. For instance if someone is abusing the connection and taking up huge amounts of bandwith we can turn off their access in FAS. Uses include native applications which notify users when events happen. Things like notification icons and bubbles can for instance tell a user that their build is done without them having to load up a web page. We can eventually open this up to trusted external entities so that they can route Fedora messages to their users without taking up too much of our bandwidth (e.g. OLPC/Sugar Labs would provide notifications to their users instead of everyone subscribing to the Fedora Servers).
Other Brokers
Other brokers can be setup to spider the notifications for load balancing or setting up different security profiles. For instance we may want to have a broker for new and third party Fedora Infrastructure pieces where their interfaces may change significantly and in general can not be trusted as much as the established infrastructure pieces. As the piece becomes more stable it can be moved to the main Infrastructure broker.
Fedora AMQP Standards
Package
A package identifies a service. All packages must be unique and application should not trample on other applications package names. This is mostly avoided by the physical setup and can be locked down using different authentication tokens for each service, (or we can just implicitly trust internal services to be configured correctly and not trample on other's name spaces). All packages originating from Fedora Infrastructure should be prefixed with org.fedoraproject and end with their service name. For example:
org.fedoraproject.koji
In the above example koji is the service name.
Events
Event names can not contain any period characters. They are used by the client to route to the correct callback handler. For example:
successful_build
In the above example koji is sending the successful_build signal.
Subscribing
Since we want to leave most of the QMF complexity to a library and bring more standardization for our particular use case, here is a conceptual API for subscribing to a signal:
context = MessagingContext("fcomm.messaging.fedoraproject.org")
context.set_auth_plain(username, pass)
context.subscribe("org.fedoraproject.koji"
"successful_build", process_successful_build,
"failed_build", process_failed_build)
As you notice we first create a context and set it to point to a broker and use plain authentication (we could use other auth methods too). Now we can subscribe to both the successful_build and failed_build events of the org.fedoraproject.koji package.
In QMF the code would look something like this:
class BuildEventConsole(Console):
def event(self, broker, event):
class_key = event.getClassKey()
event_str = class_key.getPackageName() + ':' + class_key.getClassName()
if event_str == 'org.fedoraproject.koji:successful_build':
self.process_successful_build(event)
elif event == 'org.fedoraproject.koji:failed_build':
self.process_failed_build(event)
build_console = BuildEventConsole()
sess = Session(build_console, manageConnections=True, rcvObjects=False, rcvHeartbeats=False)
broker = sess.addBroker('amqp://fcomm.messaging.fedoraproject.org')
Reading arguments sent in the payload is done via the QMF event object:
def process_successful_build(event):
args = event.getArguments()
build_id = args['build_id']
Publishing
QMF Agents need to register a schema of their events. FIXME: Need to research the Schema format more as the docs seem to exclude the info for Event Classes. Do we even need a schema for events?
We can look at a theoretical QMF Schema for koji:
<schema package="org.fedoraproject.koji"> </schema>
Implementing the fedora infrastructure message bus in QMF is complicated by the absence of a python API for QMF Agents.
Payload
The payload should contain the same row information that can be retrieved via the services REST/XML-RPC API using the primary key.
Further Routing Options
Sometimes we don't want to listen to all signals from a particular domain. For instance if I am just looking to be notified of builds I started or builds on a particular package. AMQP allows us to route based on arbitrary header key value pairs as well as the payload content. Need to investigate QMF event routing options in more detail.