Bacula basic configuration
Description
Bacula is an enterprise-grade backup utility. This HowTo explains how to set up bacula on Fedora while respecting Fedora's configuration way.
Applicable to Fedora Versions
- Fedora 12+
Requirements
Bacula supports a few database backends, so, you will need to choose one. On this document, I will choose the mysql backend. Clients do not need a database backend.
Also, you will need to decide which console(s) you want and configure them. I will choose the commandline console.
Storage, database and director could be distributed but, in this case, everything will be managed on the same server.
Server requirements
bacula-commonbacula-consolebacula-director-commonbacula-director-mysqlbacula-sysconfdir- NOTE: Package no longer offered in Fedora 18bacula-storage-commonbacula-storage-mysqlmysql-server
Client's requirements
bacula-client
Concepts and definitions
Basic description of bacula
The basic system comprises three components: the director, the file daemon and the storage daemon. To take them in reverse order, the storage daemon takes data from the file daemon and stores it wherever directed. The file daemon gets the data (files) to be backed up and passes it to the storage daemon. The director then does the rest of the work; that is, defines the task to be performed and the schedule for them to be performed. The basic unit for a backup is the job. This describes what is to be backed-up, when it is to occur and where the data is to be stored.
Some definitions
Volume - basic unit of storage, e.g. a tape, a dvd, a file on a hard drive.
Pool - a collection of volumes, usually used for the same purpose.
FileSet - the files to be backed up.
Job - the overall definition of the work to be performed.
Catalogue - storage area for information about all jobs that have run.
Full Backup - every file in the FileSet is to be copied.
Incremental - a backup that contains all files that have changed since the last full, differential or incremental backup.
Differential - a backup that contains all files that have changed since the last full backup.
Configuration files
To configure each component there is a .conf file in /etc/bacula. Each file defines the interconnectivity with the others, so you need make sure all the passwords agree one with another (you'll see what I mean when you look at the details). bacula-sd.conf defines the storage devices that you want to use, and bacula-fd.conf merely defines itself. The main work is done in bacula-dir.conf, which sets up the everything else. The configuration files are used to define those components that are to be run automatically: ad-hoc jobs can be run through the console.
Workflow
The method of operation for bacula is that the requisite data is stored on Volumes, which are essentially container files stored on differing media. These volumes are organized into Pools in a many to one relationship. Filesets are the collections of files that you want to backup using the same volumes. The timing for preforming backups are defined using Schedules, and all these are tied together as jobs, which define the pool (and hence volumes) to be used to create backups of the files defined within a fileset at a particular schedule.
Doing the Work
Configuring the server
- Install mysql-server:
su -c 'yum install mysql-server'
- Install the relevant bacula packages
su -c 'yum install bacula-common \ bacula-console bacula-director-common \ bacula-director-mysql bacula-storage-common \ bacula-storage-mysql'
- Start the mysql server
su -c 'service mysqld start'
- Grant privileges to the bacula user
su -c '/usr/libexec/bacula/grant_mysql_privileges'
- Create the database
su -c '/usr/libexec/bacula/create_mysql_database'
- Create the necessary tables
su -c '/usr/libexec/bacula/make_mysql_tables'
- Add a strong password to the bacula user
su -c 'mysql -u root'
UPDATE mysql.user SET Password=PASSWORD('Somes7r0nGp4s5wrD') WHERE User='bacula';
FLUSH PRIVILEGES;
Passwords
Passwords were the confusing part until now. This diagram will help you understand.
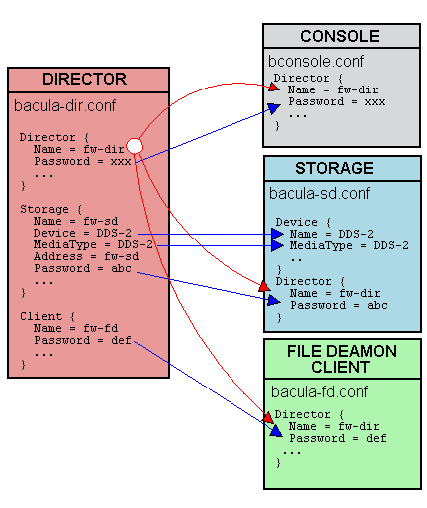
- Set /etc/bacula/bacula-dir passwords
Director { # define myself
Name = bacula-dir
DIRport = 9101 # where we listen for UA connections
QueryFile = "/usr/libexec/bacula/query.sql"
WorkingDirectory = "/var/spool/bacula"
PidDirectory = "/var/run"
Maximum Concurrent Jobs = 1
Password = "SomeReallyCoolDirPassword" # Console password
Messages = Daemon
}
JobDefs {
Name = "DefaultJob"
Type = Backup
Level = Incremental
Client = bacula-fd
FileSet = "Full Set"
Schedule = "WeeklyCycle"
Storage = File
Messages = Standard
Pool = Default
Priority = 10
}
#
# Define the main nightly save backup job
# By default, this job will back up to disk in /tmp
Job {
Name = "BackupClient1"
JobDefs = "DefaultJob"
Write Bootstrap = "/var/spool/bacula/Client1.bsr"
}
#Job {
# Name = "BackupClient2"
# Client = bacula2-fd
# JobDefs = "DefaultJob"
# Write Bootstrap = "/var/spool/bacula/Client2.bsr"
#}
# Backup the catalog database (after the nightly save)
Job {
Name = "BackupCatalog"
JobDefs = "DefaultJob"
Level = Full
FileSet="Catalog"
Schedule = "WeeklyCycleAfterBackup"
# This creates an ASCII copy of the catalog
# WARNING!!! Passing the password via the command line is insecure.
# see comments in make_catalog_backup for details.
# Arguments to make_catalog_backup are:
# make_catalog_backup <database-name> <user-name> <password> <host>
RunBeforeJob = "/usr/libexec/bacula/make_catalog_backup bacula bacula ASlickDBPasswordWithNumbersAndAll"
# This deletes the copy of the catalog
RunAfterJob = "/usr/libexec/bacula/delete_catalog_backup"
Write Bootstrap = "/var/spool/bacula/BackupCatalog.bsr"
Priority = 11 # run after main backup
}
#
# Standard Restore template, to be changed by Console program
# Only one such job is needed for all Jobs/Clients/Storage ...
#
Job {
Name = "RestoreFiles"
Type = Restore
Client=bacula-fd
FileSet="Full Set"
Storage = File
Pool = Default
Messages = Standard
Where = /tmp/bacula-restores
}
# List of files to be backed up
FileSet {
Name = "Full Set"
Include {
Options {
signature = MD5
}
#
# Put your list of files here, preceded by 'File =', one per line
# or include an external list with:
#
# File = <file-name
#
# Note: / backs up everything on the root partition.
# if you have other partitions such as /usr or /home
# you will probably want to add them too.
#
# By default this is defined to point to the Bacula binary
# directory to give a reasonable FileSet to backup to
# disk storage during initial testing.
#
File = /usr/sbin
}
#
# If you backup the root directory, the following two excluded
# files can be useful
#
Exclude {
File = /var/spool/bacula
File = /tmp
File = /proc
File = /tmp
File = /.journal
File = /.fsck
}
}
#
# When to do the backups, full backup on first sunday of the month,
# differential (i.e. incremental since full) every other sunday,
# and incremental backups other days
Schedule {
Name = "WeeklyCycle"
Run = Full 1st sun at 23:05
Run = Differential 2nd-5th sun at 23:05
Run = Incremental mon-sat at 23:05
}
# This schedule does the catalog. It starts after the WeeklyCycle
Schedule {
Name = "WeeklyCycleAfterBackup"
Run = Full sun-sat at 23:10
}
# This is the backup of the catalog
FileSet {
Name = "Catalog"
Include {
Options {
signature = MD5
}
File = /var/spool/bacula/bacula.sql
}
}
# Client (File Services) to backup
Client {
Name = bacula-fd
Address = client.example.com
FDPort = 9102
Catalog = MyCatalog
Password = "TheCoolFileDaemonPassword" # password for FileDaemon
File Retention = 30 days # 30 days
Job Retention = 6 months # six months
AutoPrune = yes # Prune expired Jobs/Files
}
# Definition of file storage device
Storage {
Name = File
# Do not use "localhost" here
Address = storage.example.com # N.B. Use a fully qualified name here
SDPort = 9103
Password = "TheStorageDaemonPassword"
Device = FileStorage
Media Type = File
}
# Generic catalog service
Catalog {
Name = MyCatalog
# Uncomment the following line if you want the dbi driver
# dbdriver = "dbi:sqlite3"; dbaddress = 127.0.0.1; dbport =
dbname = "bacula"; dbuser = "bacula"; dbpassword = "ASlickDBPasswordWithNumbersAndAll"
}
# Reasonable message delivery -- send most everything to email address
# and to the console
Messages {
Name = Standard
#
# NOTE! If you send to two email or more email addresses, you will need
# to replace the %r in the from field (-f part) with a single valid
# email address in both the mailcommand and the operatorcommand.
# What this does is, it sets the email address that emails would display
# in the FROM field, which is by default the same email as they're being
# sent to. However, if you send email to more than one address, then
# you'll have to set the FROM address manually, to a single address.
# for example, a 'no-reply@mydomain.com', is better since that tends to
# tell (most) people that its coming from an automated source.
#
mailcommand = "/usr/sbin/bsmtp -h localhost -f \"\(Bacula\) \<%r\>\" -s \"Bacula: %t %e of %c %l\" %r"
operatorcommand = "/usr/sbin/bsmtp -h localhost -f \"\(Bacula\) \<%r\>\" -s \"Bacula: Intervention needed for %j\" %r"
mail = root@localhost = all, !skipped
operator = root@localhost = mount
console = all, !skipped, !saved
#
# WARNING! the following will create a file that you must cycle from
# time to time as it will grow indefinitely. However, it will
# also keep all your messages if they scroll off the console.
#
append = "/var/spool/bacula/log" = all, !skipped
catalog = all
}
#
# Message delivery for daemon messages (no job).
Messages {
Name = Daemon
mailcommand = "/usr/sbin/bsmtp -h localhost -f \"\(Bacula\) \<%r\>\" -s \"Bacula daemon message\" %r"
mail = root@localhost = all, !skipped
console = all, !skipped, !saved
append = "/var/log/bacula.log" = all, !skipped
}
# Default pool definition
Pool {
Name = Default
Pool Type = Backup
Recycle = yes # Bacula can automatically recycle Volumes
AutoPrune = yes # Prune expired volumes
Volume Retention = 365 days # one year
}
# Scratch pool definition
Pool {
Name = Scratch
Pool Type = Backup
}
#
# Restricted console used by tray-monitor to get the status of the director
#
Console {
Name = bacula-mon
Password = "TheDirMonitorPassword"
CommandACL = status, .status
}
- Set /etc/bacula/bacula-fd passwords
Director {
Name = bacula-dir
Password = "TheCoolFileDaemonPassword"
}
#
# Restricted Director, used by tray-monitor to get the
# status of the file daemon
#
Director {
Name = bacula-mon
Password = "ANeatFDMonitorPassword"
Monitor = yes
}
#
# "Global" File daemon configuration specifications
#
FileDaemon { # this is me
Name = bacula-fd
FDport = 9102 # where we listen for the director
WorkingDirectory = /var/spool/bacula
Pid Directory = /var/run
Maximum Concurrent Jobs = 20
}
# Send all messages except skipped files back to Director
Messages {
Name = Standard
director = bacula-dir = all, !skipped, !restored
}
- Set /etc/bacula/bacula-sd passwords
Storage { # definition of myself
Name = bacula-sd
SDPort = 9103 # Director's port
WorkingDirectory = "/var/spool/bacula"
Pid Directory = "/var/run"
Maximum Concurrent Jobs = 20
}
#
# List Directors who are permitted to contact Storage daemon
#
Director {
Name = bacula-dir
Password = "TheStorageDaemonPassword"
}
#
# Restricted Director, used by tray-monitor to get the
# status of the storage daemon
#
Director {
Name = bacula-mon
Password = "ANiceStorageDaemonMonitorPassword"
Monitor = yes
}
#
# Note, for a list of additional Device templates please
# see the directory <bacula-source>/examples/devices
# Or follow the following link:
# http://bacula.svn.sourceforge.net/viewvc/bacula/trunk/bacula/examples/devices/
#
#
# Devices supported by this Storage daemon
# To connect, the Director's bacula-dir.conf must have the
# same Name and MediaType.
#
Device {
Name = FileStorage
Media Type = File
Archive Device = /tmp
LabelMedia = yes; # lets Bacula label unlabeled media
Random Access = Yes;
AutomaticMount = yes; # when device opened, read it
RemovableMedia = no;
AlwaysOpen = no;
}
#
# Send all messages to the Director,
# mount messages also are sent to the email address
#
Messages {
Name = Standard
director = bacula-dir = all
}
Firewall
- Open up the relevant iptables port for the director
su -c 'iptables -A INPUT -m conntrack --ctstate NEW -m tcp \ -p tcp --dport 9101 -j ACCEPT'
- Open up the relevant iptables port for the storage
su -c 'iptables -A INPUT -m conntrack --ctstate NEW -m tcp \ -p tcp --dport 9103 -j ACCEPT'
Services
- Activate the services on boot
su -c 'chkconfig bacula-sd on' su -c 'chkconfig bacula-dir on' su -c 'chkconfig bacula-fd on'
- Start the storage and dir services
su -c 'service bacula-sd start' su -c 'service bacula-dir start' su -c 'service bacula-fd start'
Configuring the clients
- Install the bacula client
su -c 'yum install bacula-client'
Passwords
- Configure the client's and monitor's names, addresses and passwords. These ones need to be present in the server configuration so, keep track of the passwords and names.
#
# Default Bacula File Daemon Configuration file
#
# For Bacula release 3.0.3 (18 October 2009) -- redhat
#
# There is not much to change here except perhaps the
# File daemon Name to
#
#
# List Directors who are permitted to contact this File daemon
#
Director {
Name = bacula-dir
Password = "fd_password" # change to a nice and strong password
}
#
# Restricted Director, used by tray-monitor to get the
# status of the file daemon
#
Director {
Name = bacula-mon
Password = "mon_fd_password" # change to a nice and strong password
Monitor = yes
}
#
# "Global" File daemon configuration specifications
#
FileDaemon { # this is me
Name = bacula-fd
FDport = 9102 # where we listen for the director
WorkingDirectory = /var/spool/bacula
Pid Directory = /var/run
Maximum Concurrent Jobs = 20
}
# Send all messages except skipped files back to Director
Messages {
Name = Standard
director = bacula-dir = all, !skipped, !restored
}
Firewall
- Open up the relevant firewall port; in this case, 9102
su -c 'iptables -A INPUT -m conntrack --ctstate NEW -m tcp \ -p tcp --dport 9102 -j ACCEPT'
Troubleshooting
How to test
Common problems and fixes
Using MySQL backend in Fedora 17+
Starting in Fedora 17, Bacula RPMs from the official repository are shipped with postgresql support by default. To use the MySQL backend, as shown in the article, do the following:
- Stop Bacula services if they are running:
su -c 'service bacula-dir stop' su -c 'service bacula-fd stop' su -c 'service baucla-sd stop'
- Change the "libbaccats" (the catalogue library) symlink to the real library. To change to a different backend, issue the following command:
su -c 'alternatives --config libbaccats.so'
There are 3 programs which provide 'libbaccats.so'. You'll see something like the following:
Selection Command ----------------------------------------------- 1 /usr/lib64/libbaccats-mysql.so 2 /usr/lib64/libbaccats-sqlite3.so *+ 3 /usr/lib64/libbaccats-postgresql.so Enter to keep the current selection[+], or type selection number:
Select 1 to specify the MySQL backend.[1]
- Go to the configuration scripts location
cd /usr/libexec/bacula
- Change the
default_db_typefrompostgrestomysqlin files:- create_bacula_database
- drop_bacula_database
- drop_bacula_tables
- grant_bacula_privileges
- make_bacula_tables
- update_bacula_tables
- make_catalog_backup
sed -i -e 's/default_db_type=postgresql/default_db_type=mysql/g' *
- Start bacula services again:
su -c 'service bacula-dir start' su -c 'service bacula-fd start' su -c 'service baucla-sd start'
Thanks to Pierangelo on the forums.
More Information
Disclaimer
I haven't had the opportunity to test this HowTo since I lack of a networked PC to do it, so you may run into problems, if you do, come to #fedora on irc.freenode.net or leave me messages so I know what's up and, if You know what You're doing, then make the necesary changes with cool comments and, maybe, some discussion.
Feel free to propose changes and stuff.

